Ancient Egypt: an introduction
Read Now >Chapter 8
The world of ancient Egypt
Few civilizations have enjoyed the longevity and global cultural reach of ancient Egypt. Their distinct visual expressions, writing system, and imposing monuments are instantly recognizable by viewers all around the world even today—put simply, their branding was on point.
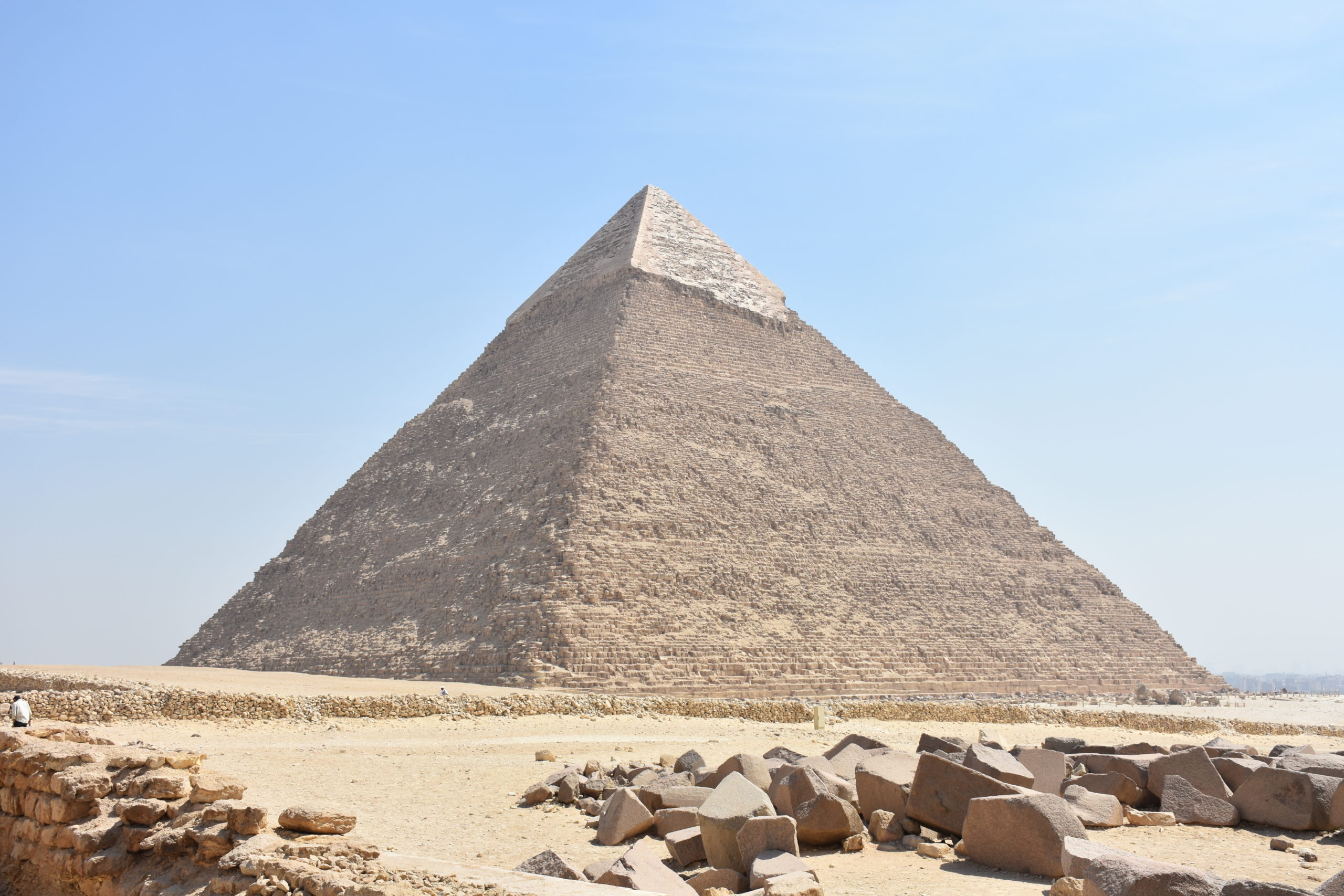

Pyramid of Khafre, Egypt (photo: MusikAnimal, CC BY-SA 3.0)
Despite portraying significant stability over a vast period of time, their civilization was not as static as it may appear at first glance, particularly if viewed through our modern eyes and cultural perspectives. Instead, the culture was dynamic even as it revolved around a stable core of imagery and concepts. The ancient Egyptians adjusted to new experiences, constantly adding to their complex beliefs about the divine and terrestrial realms, and how they interact. This flexibility, wrapped around a base of consistency, was part of the reason ancient Egypt survived for millennia and continues to fascinate.
Read an introductory essay about ancient Egypt

/1 Completed
The Natural World of Egypt
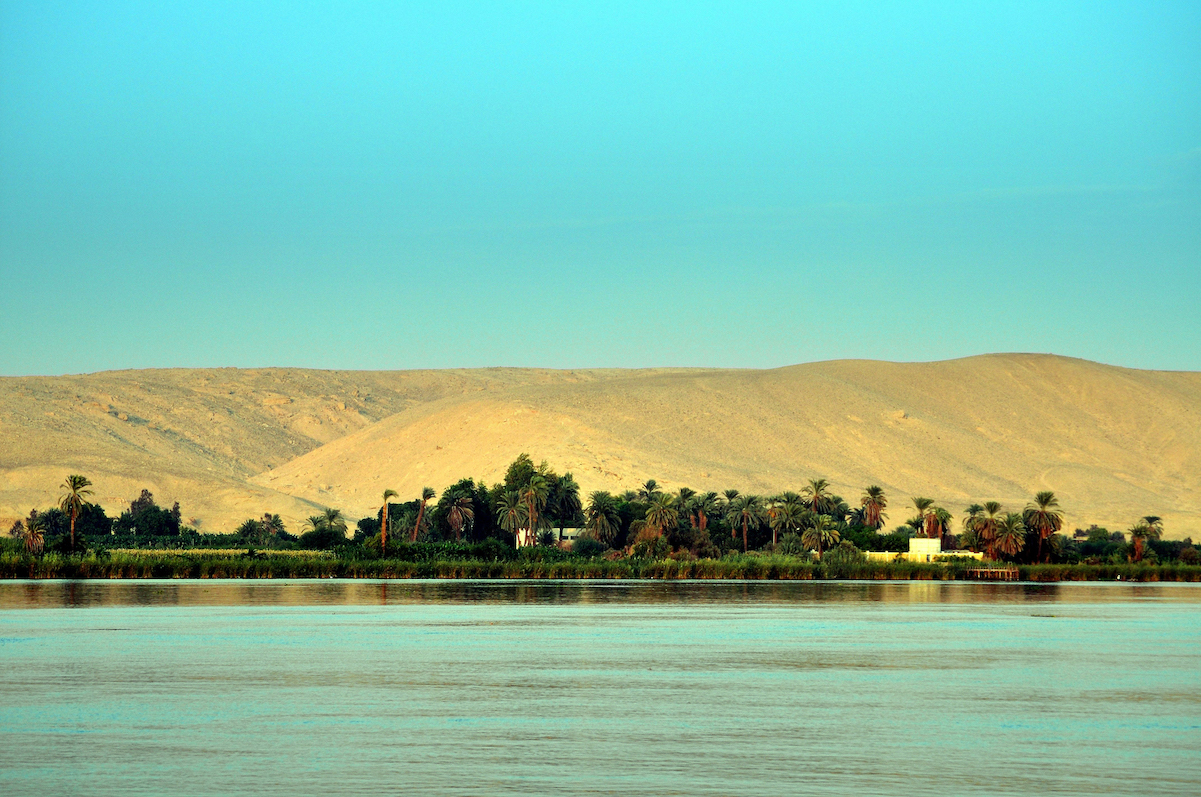

View of the Nile River, Egypt (photo: Badics, CC BY-SA 3.0)
With the blazing sun above, flanked by vast seas of shifting sand, and fed by the life-giving Nile River (which hid frightening creatures beneath its dark waters), the natural world of Egypt was inherently beautiful but also potentially deadly. Outside the lush river valley, there was little protection from the ever-dominant sun, whose intensity was both feared and revered. The deserts were home not only to many dangerous creatures, but the sands themselves were also unpredictable and constantly shifting. The clear night skies dazzled with millions of stars, some of which seemed to move of their own accord while others rose and fell at trackable intervals. The Nile, with its annual floods, brought fertility and renewal to the land, but could also overflow and wreak havoc on the villages that lined its banks. Careful observers of their environment, the Egyptians perceived divine forces in these phenomena and many of their deities, such as the powerful sun god Ra, were connected with elements from the natural world.

Hieroglyphs, detail from the White Chapel, Karnak (photo: Dr. Amy Calvert)
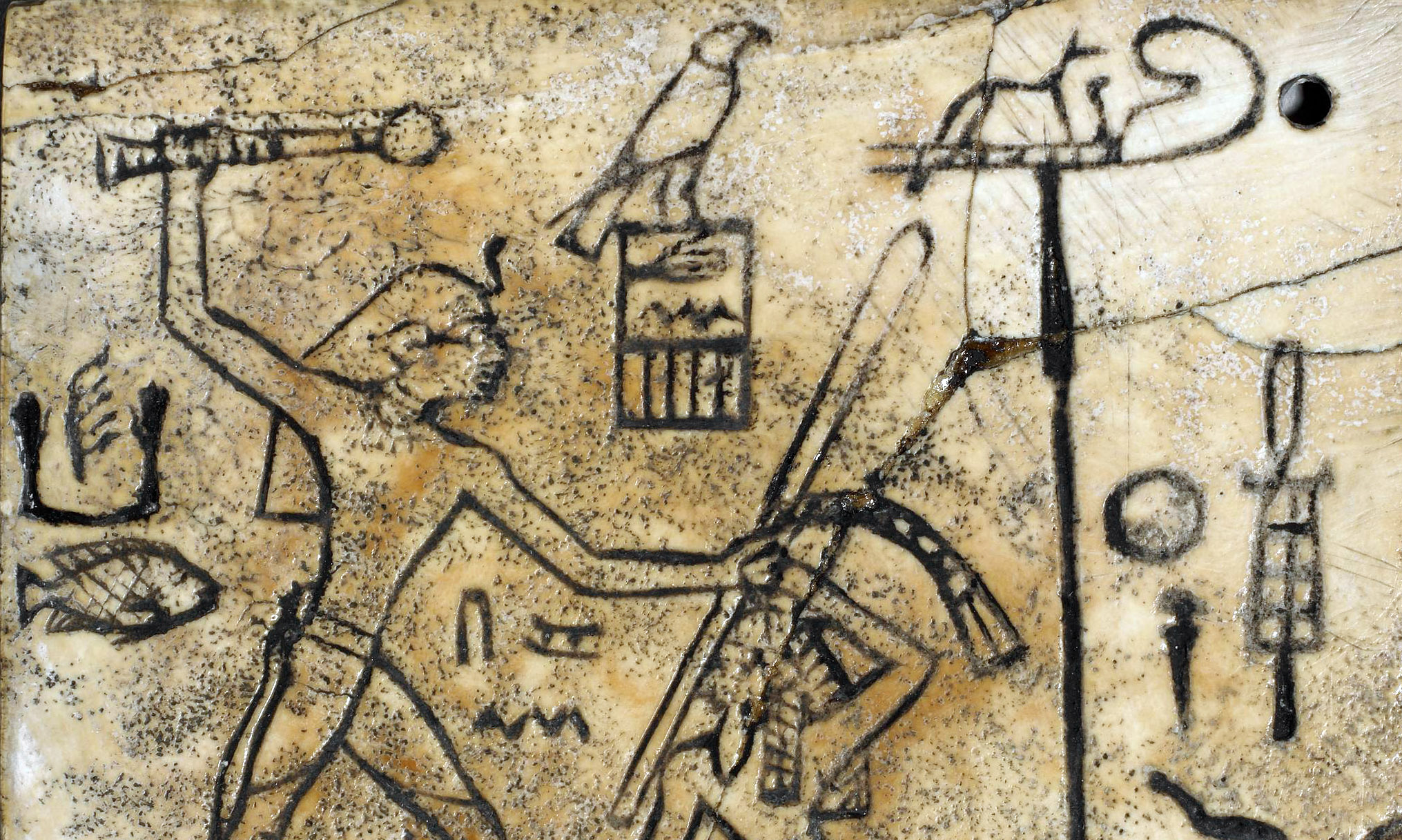
The perception of divine powers existing in the natural world was particularly true in connection with the animals that inhabited the region. There was an array of creatures that the Egyptians would have observed or interacted with on a regular basis and they feature heavily in the culture. One of the most distinctive visual attributes of Egyptian imagery is the myriad deities that were portrayed in hybrid form, with a human body and animal head. In addition, a wide range of birds, fishes, mammals, reptiles, and other creatures appear prominently in the hieroglyphic script—there are dozens of different birds alone.
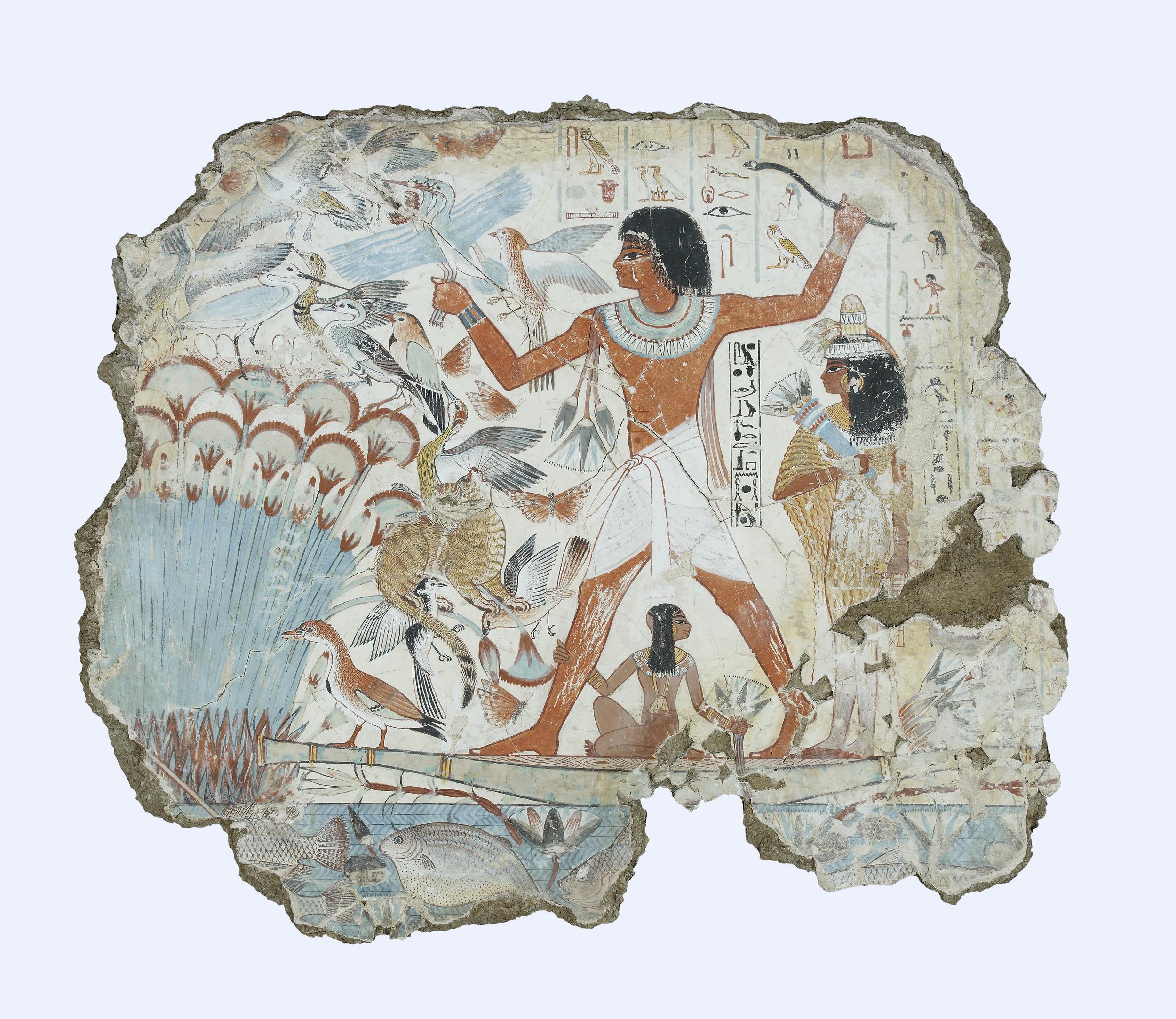

Nebamun fowling in the marshes, Tomb-chapel of Nebamun, c. 1350 B.C.E., 18th Dynasty, paint on plaster, 83 x 98 cm, Thebes (© Trustees of the British Museum)
The Nile was packed with numerous types of fish, which were recorded in great detail in fishing scenes that became a fixture in non-royal tombs. Most relief and painting throughout Egypt’s history was created for divine or mortuary settings and they were primarily intended to be functional. Many tomb scenes included the life-giving Nile and all it’s abundance with the goal of making that bounty available for the deceased in the afterlife. In addition to the array of fish, the river also teemed with far more dangerous animals, like crocodiles and hippopotami. Protective spells and magical gestures were used from early on to aid the Egyptians in avoiding those watery perils as they went about their daily lives.
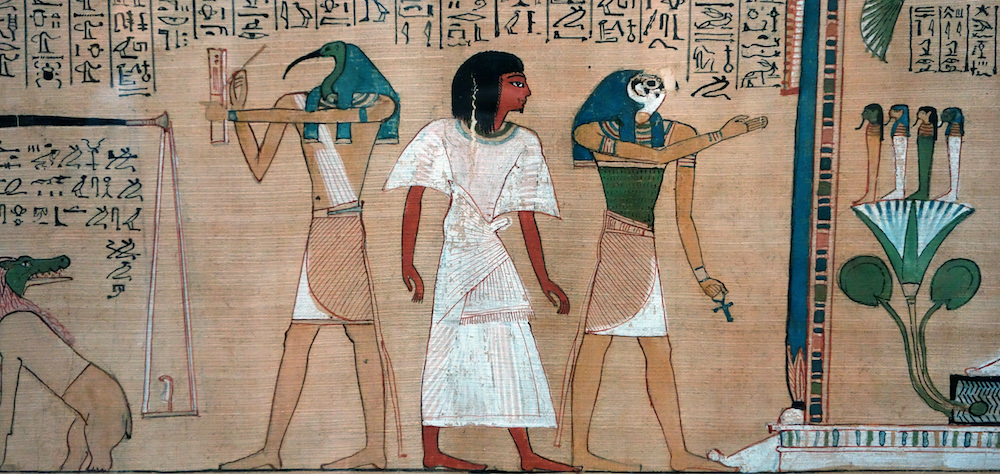

Hunefer (center) flanked by two deities: the ibis-headed Thoth (left) and the falcon-headed Horus (right), from Hunefer’s Judgement in the presence of Osiris, Book of the Dead of Hunefer, 19th Dynasty, New Kingdom, c. 1275 B.C.E., papyrus, Thebes, Egypt (British Museum)
The desert, likewise, was full of potentially dangerous creatures. Lions, leopards, jackals, cobras, and scorpions were all revered for their attributes and feared for their ferocity. Soaring above were birds of prey, like falcons who were sharp-eyed hunters, and massive vultures that consumed decaying flesh and fed it to their young. Scarab beetles also seemingly brought new life from decay and the sacred ibis with their curved beaks found sustenance hidden in the muddy banks of the Nile. All of these creatures (and many others) became closely associated with different deities very early in Egyptian history. The Egyptians did not worship animals; instead, certain animals were revered because it was believed that they were related to particular gods and thus served as earthly manifestations of those deities.
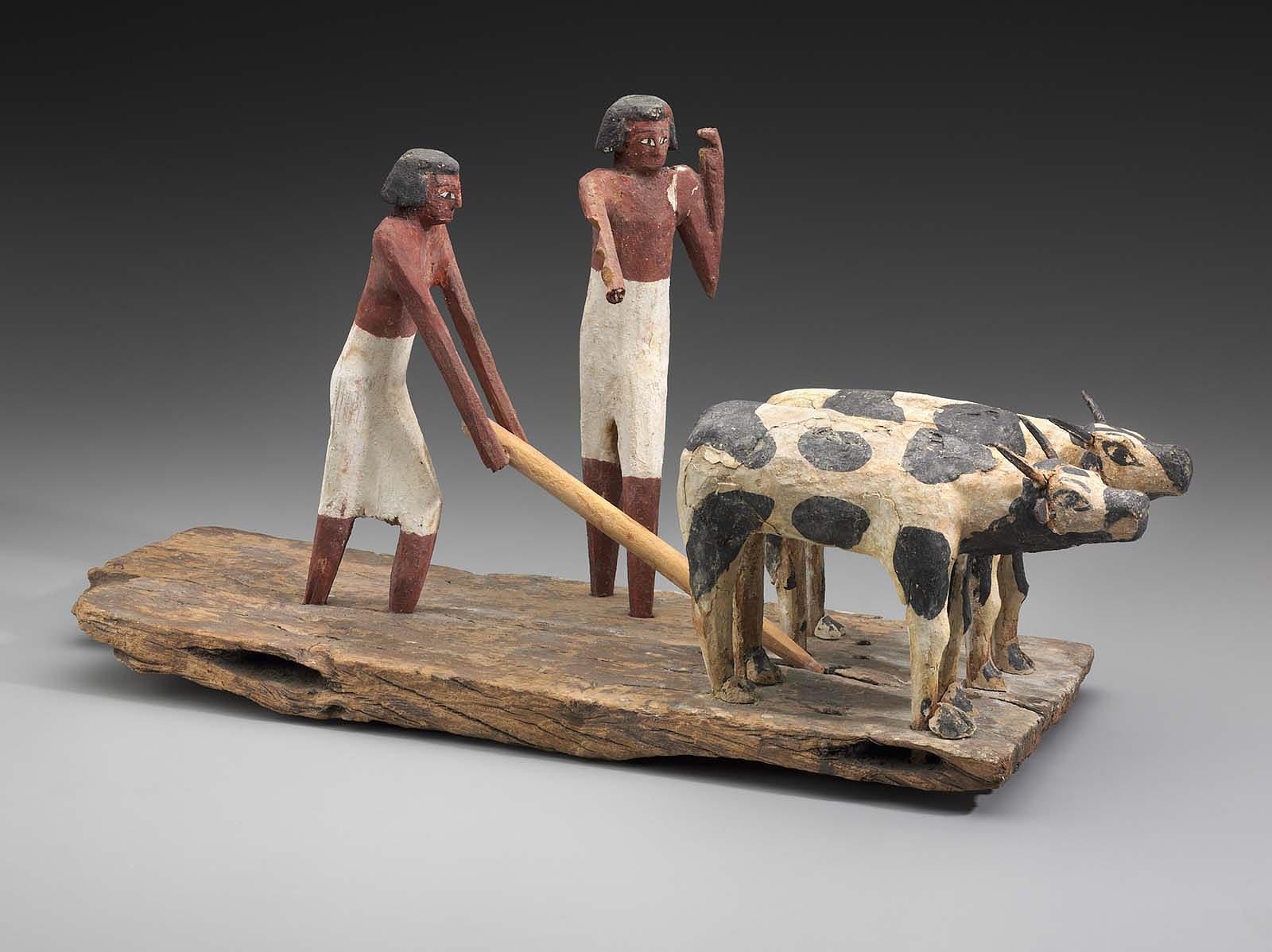

Model scene of workers ploughing a field, Middle Kingdom, late Dynasty 11, 2010–1961 B.C.E., wood, 54 cm (MFA Boston)
Even domesticated animals, such as cows, bulls, rams, and geese, became associated with deities and were viewed as vitally important. Cattle were probably the first animals to be domesticated in Egypt and domesticated cattle, donkeys, and rams appear along with wild animals on Predynastic and Early Dynastic votive objects, showing massive herds that were controlled by early rulers, demonstrating their wealth and prestige. Pastoral scenes of animal husbandry appear in numerous private tomb chapels and wooden models, providing detailed evidence of their daily practices. Herdsmen appear caring for their animals in depictions that include milking, calving, protecting the cattle as they cross the river, feeding, herding, and many other aspects of their day-to-day care.
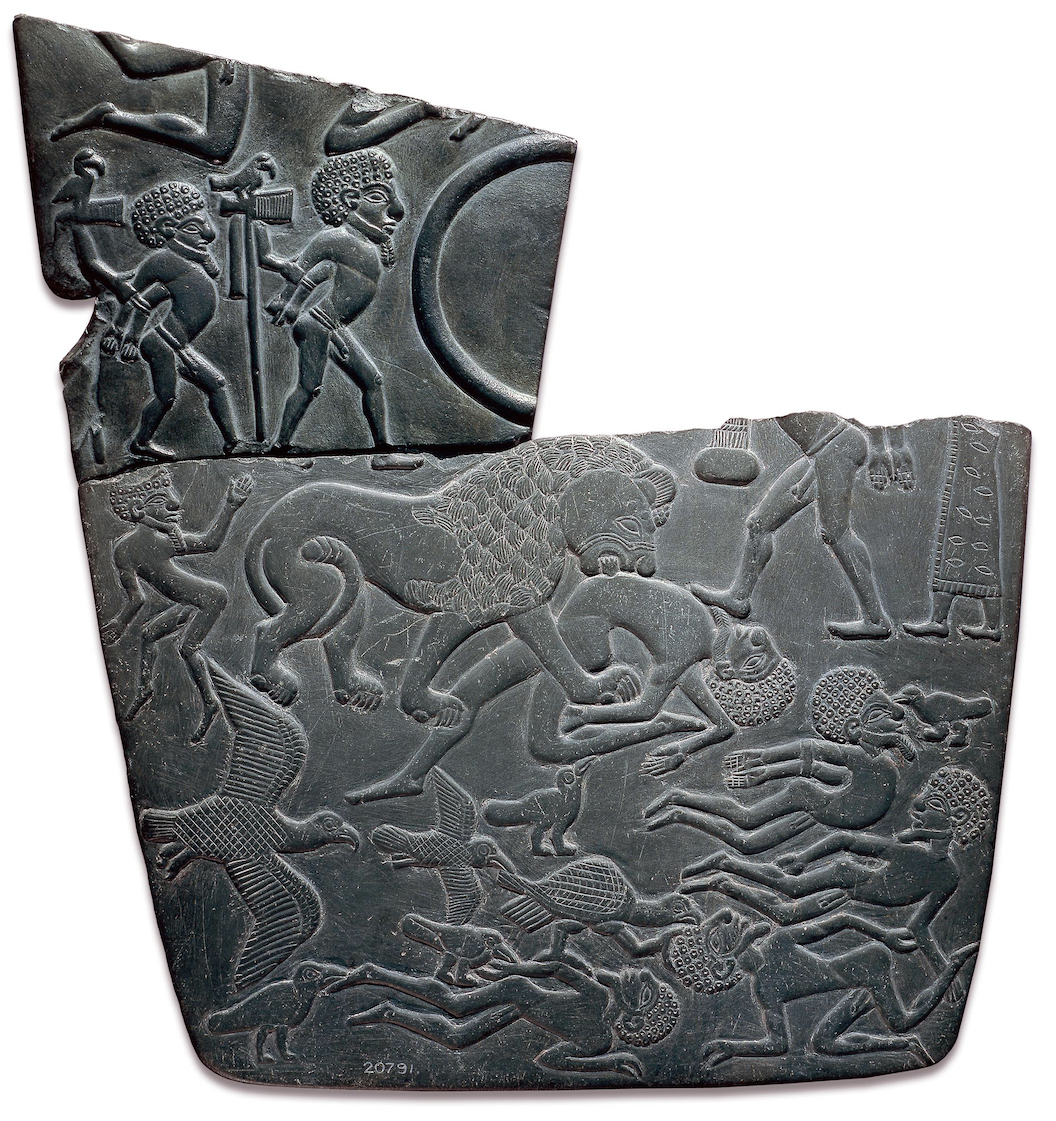

The Battlefield Palette, c. 3100 B.C.E., mudstone, found at el-Amarna, Egypt, 19.6 x 32.8 cm (© Trustees of the British Museum)
Already in the Predynastic period the king was linked with the virile wild bull, an association that continues throughout Egyptian history—one of the primary items of royal regalia was a bull tail, which appears on a huge number of pharaonic images. An early connection between the king and lions is also apparent. One scene on a Predynastic ceremonial palette (The Battlefield Palette), shows the triumphant king as a massive lion devouring his defeated foes. First Dynasty kings appear to have kept lion cubs as pets.
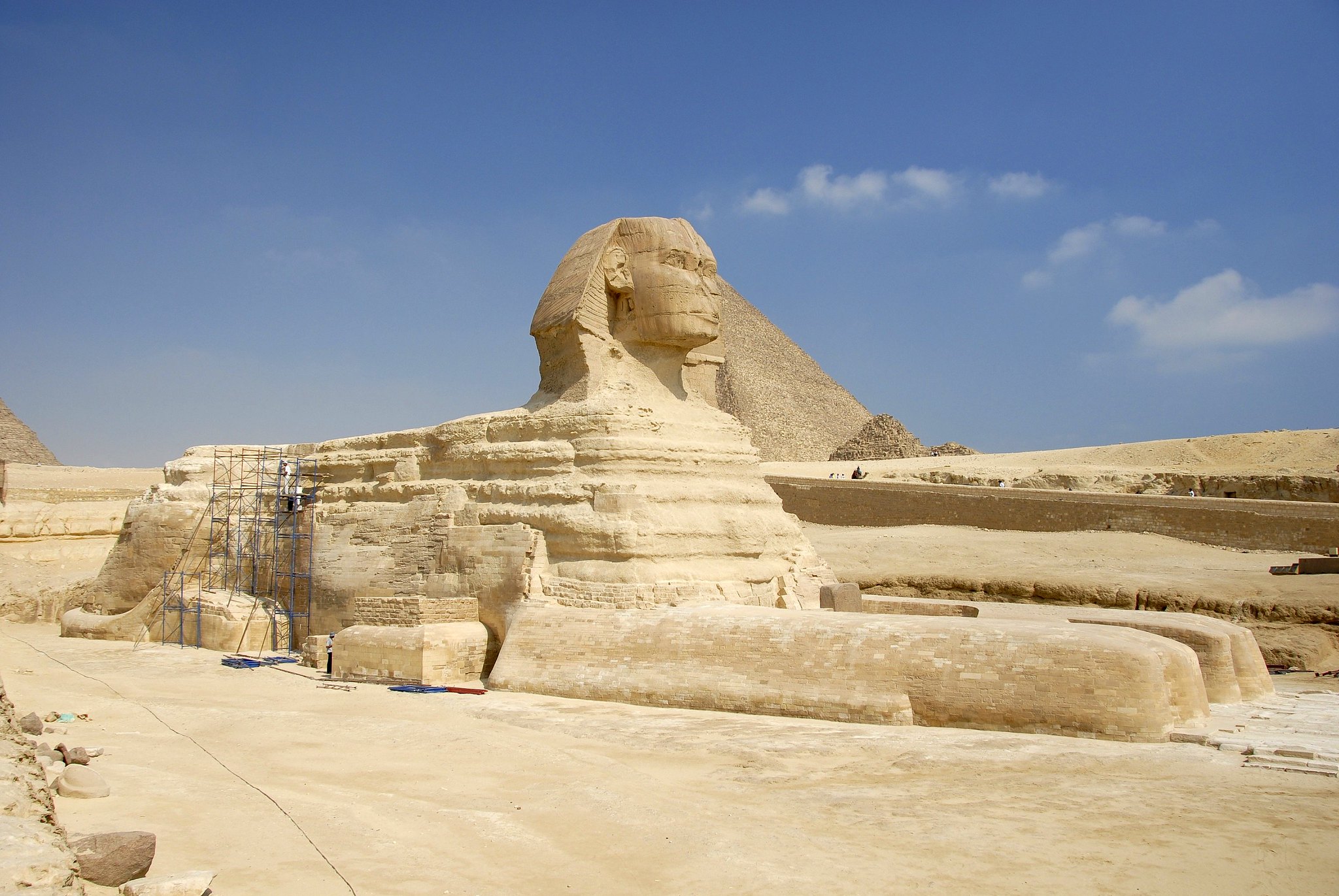

The Great Sphinx (photo: superblinkymac, CC BY-NC-ND 2.0)
In addition, lions (among other animals) were associated with the burials of some early rulers. One of the most iconic images from ancient Egypt is the massive Great Sphinx at Giza, which was sculpted from the living rock of the plateau. This fused form, with the body of a lion and the head of the king, became a common visual expression of royal power.
Historical Setting
While many of the religious and cultural characteristics of ancient Egypt were evident from very early on and continued all the way through the Roman era (contributing to overall cultural stability), sweeping conceptual developments and adoptions of external elements are also evident. Throughout ancient Egypt’s long history, periods of unified control were interspersed with moments of instability where parts of the country were controlled by different authorities. These repeated waves of political and cultural development create a decidedly complex history that spans thousands of years.
Read essays to understand the historical setting and basic characteristics of each era
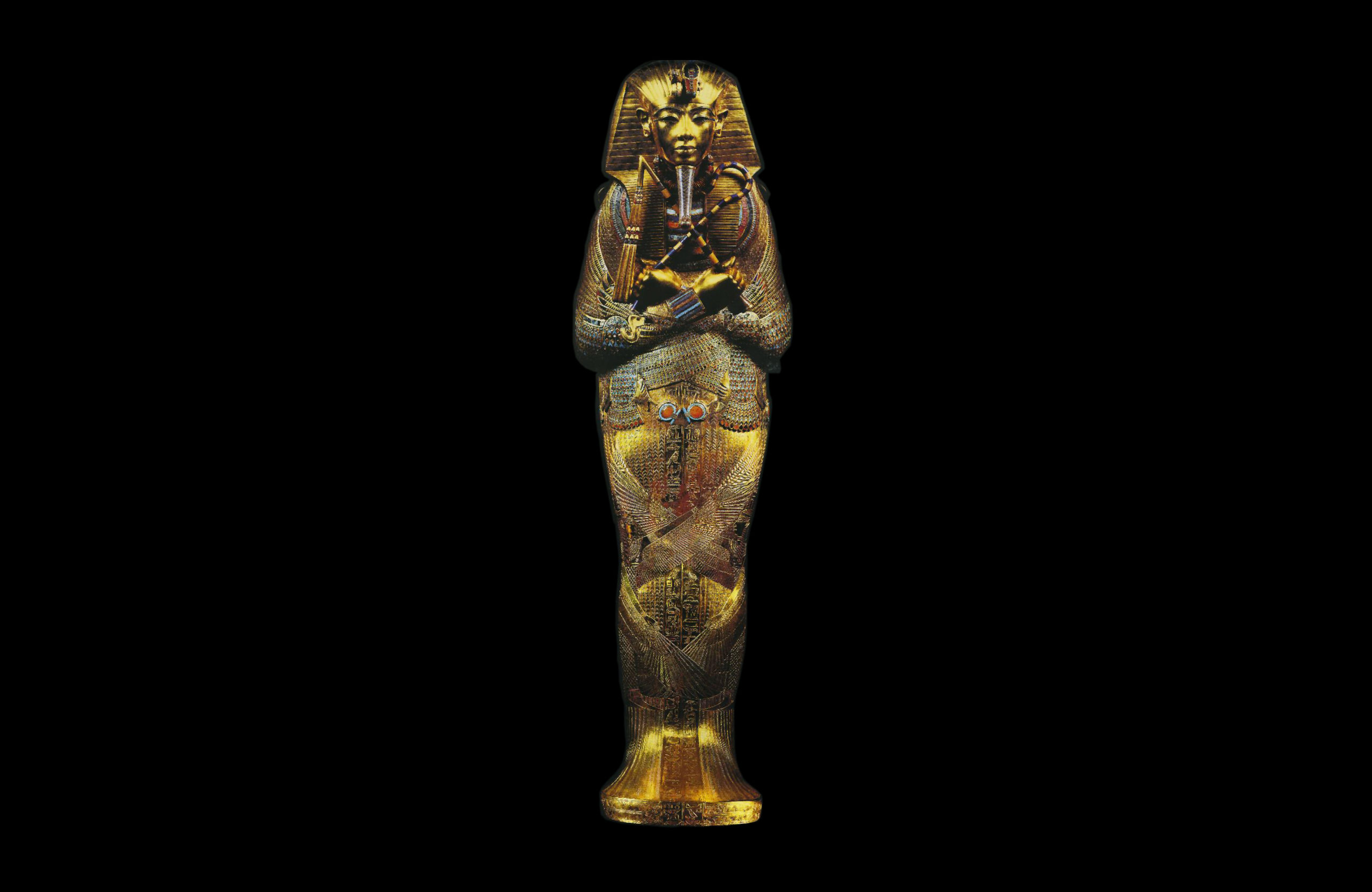
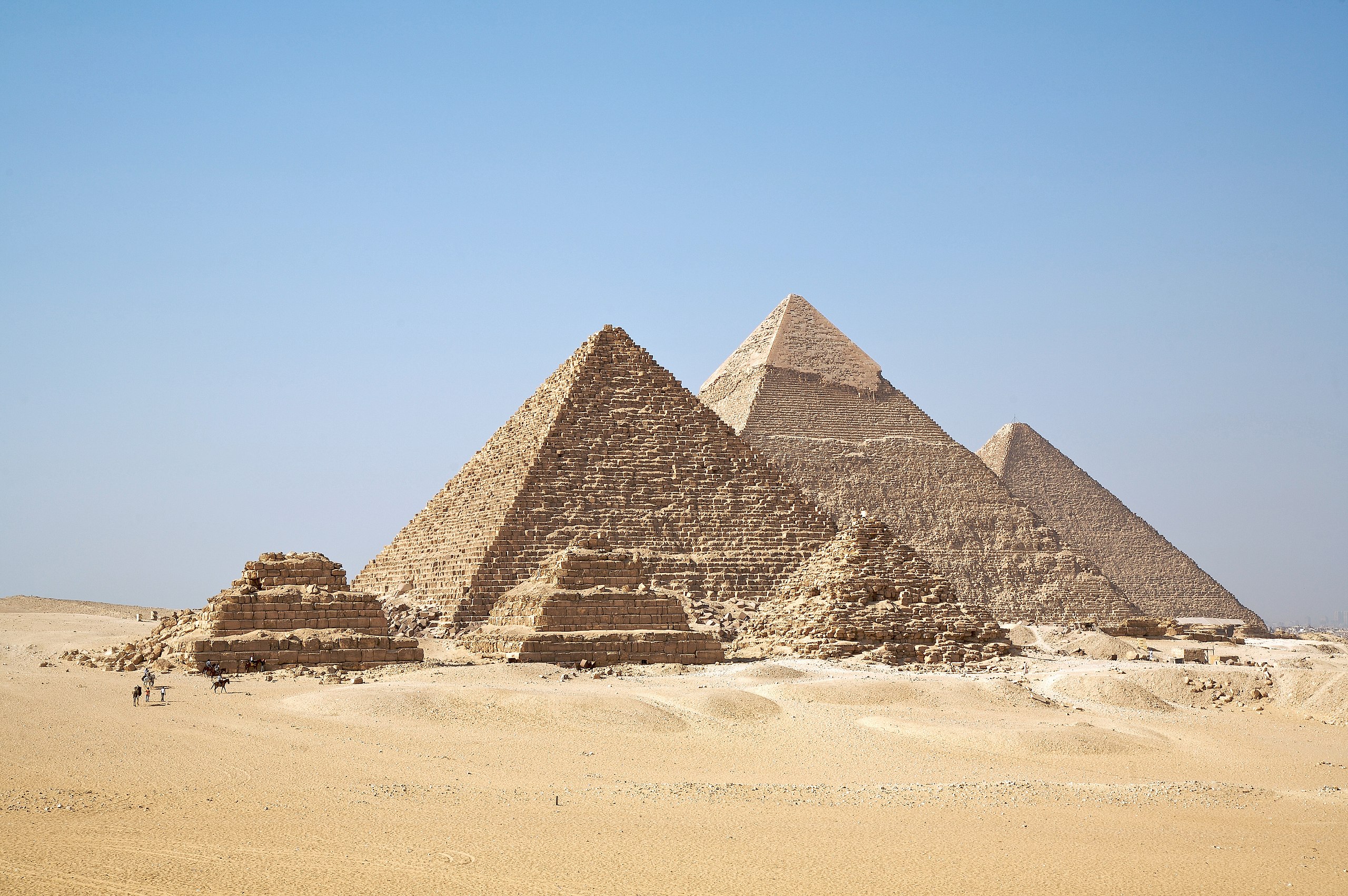
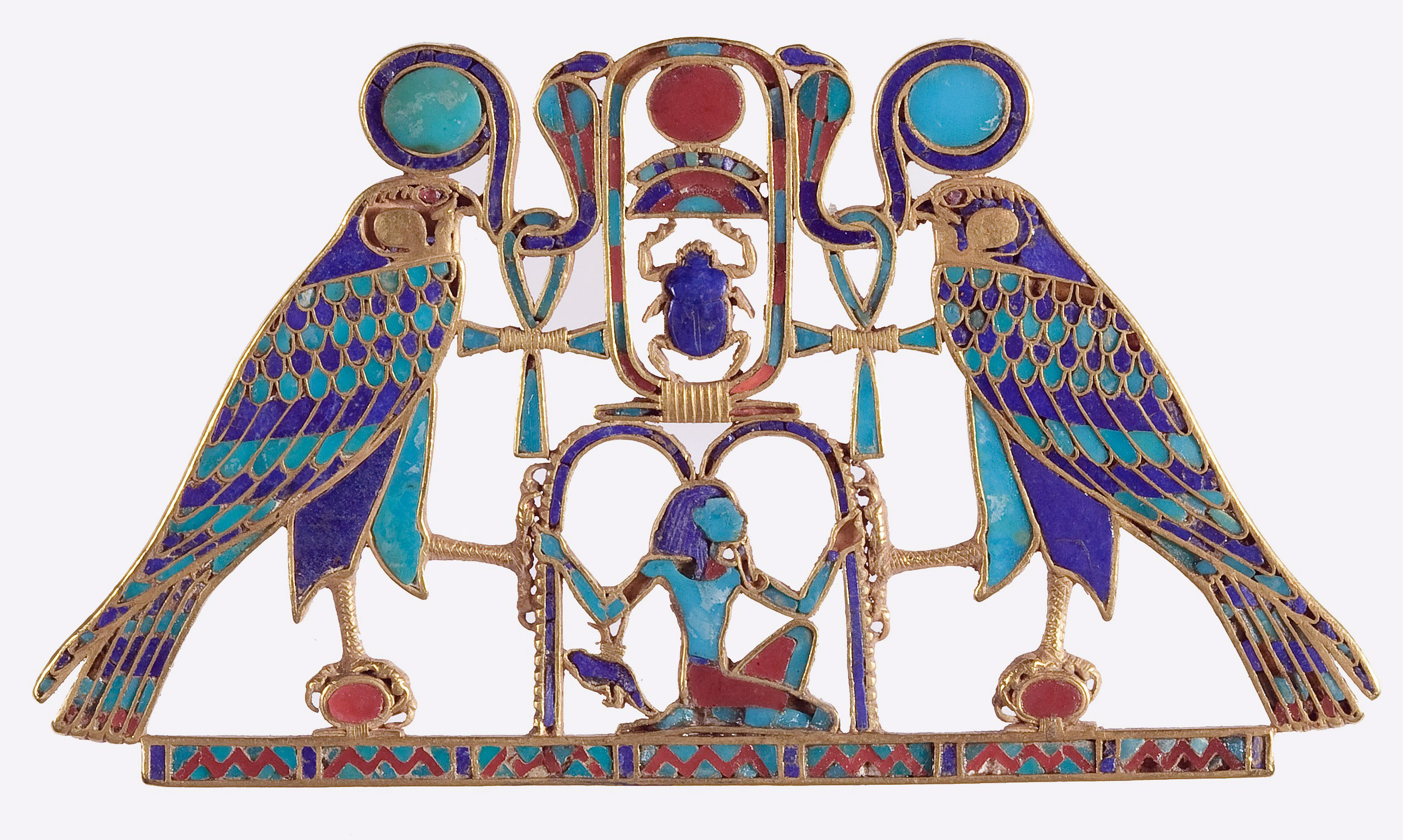
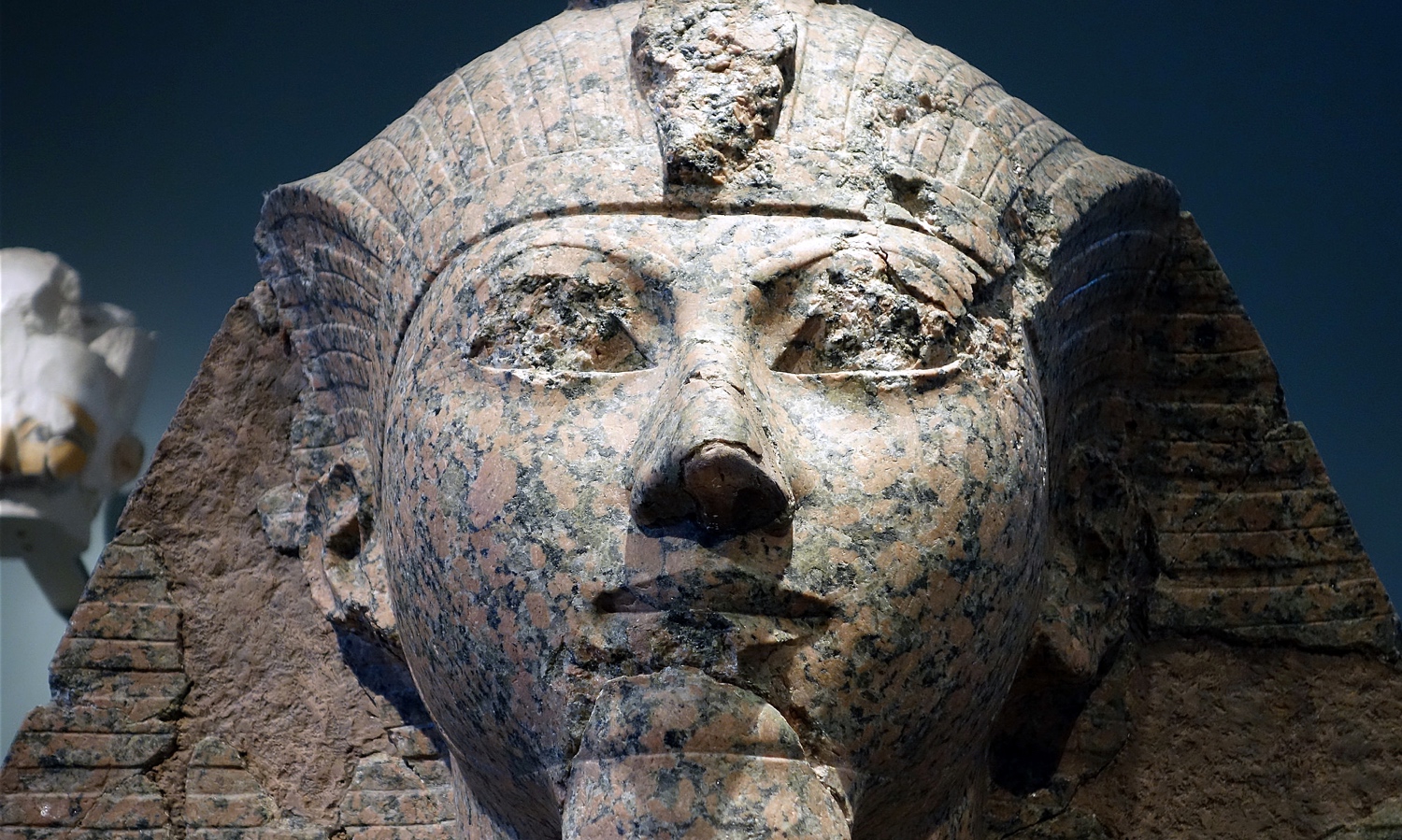





/6 Completed
Social Organization
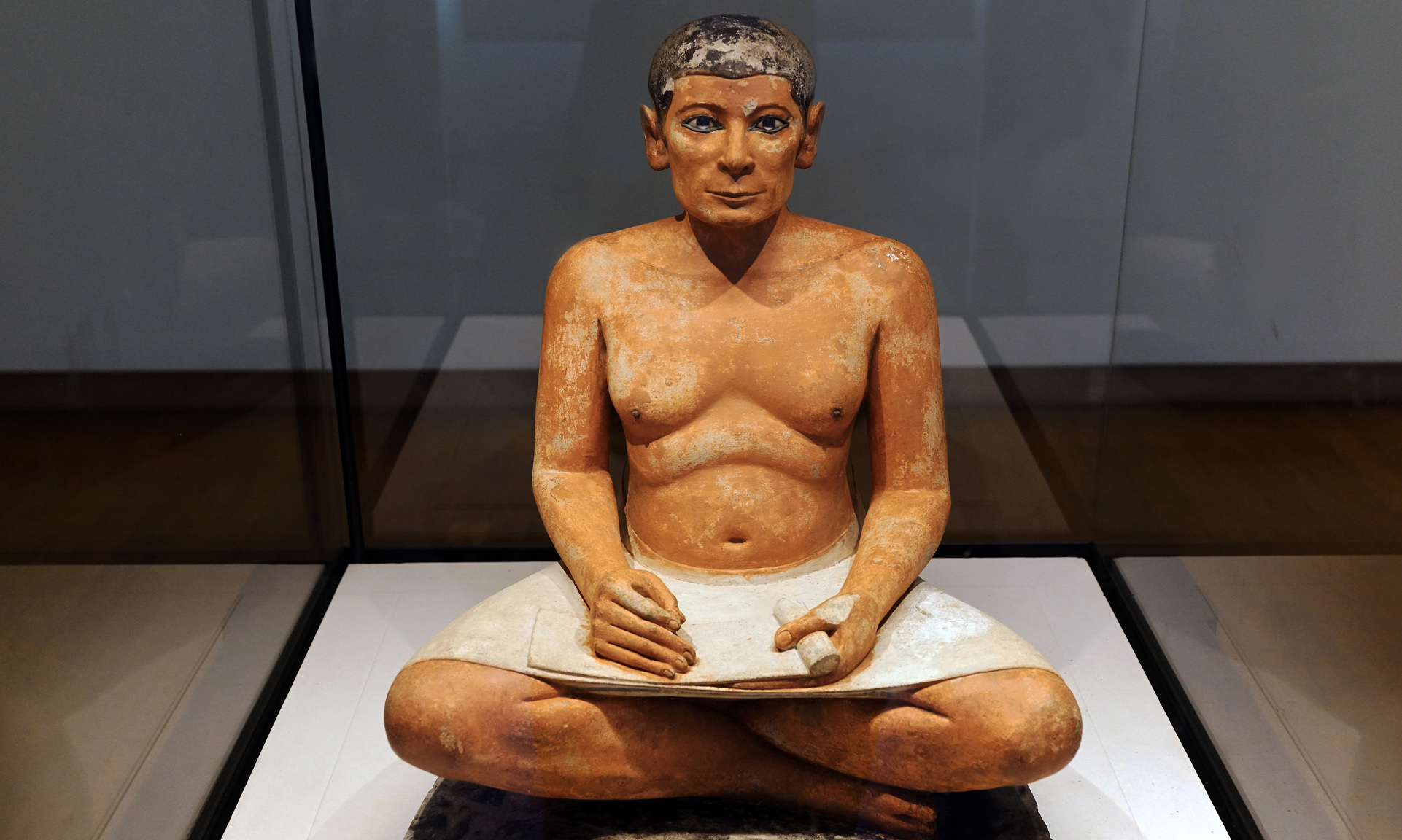
Conceptually, the Egyptian state was an absolute monarchy where the office of pharaoh itself was considered divine. The pharaoh (king) was viewed as the earthly manifestation of the god Horus, and was responsible as the supreme commander for making all decisions affecting the nation. In reality, the king stood at the head of a hierarchical administrative structure with layers of civil officials that oversaw various systems and were responsible to the king for their success.
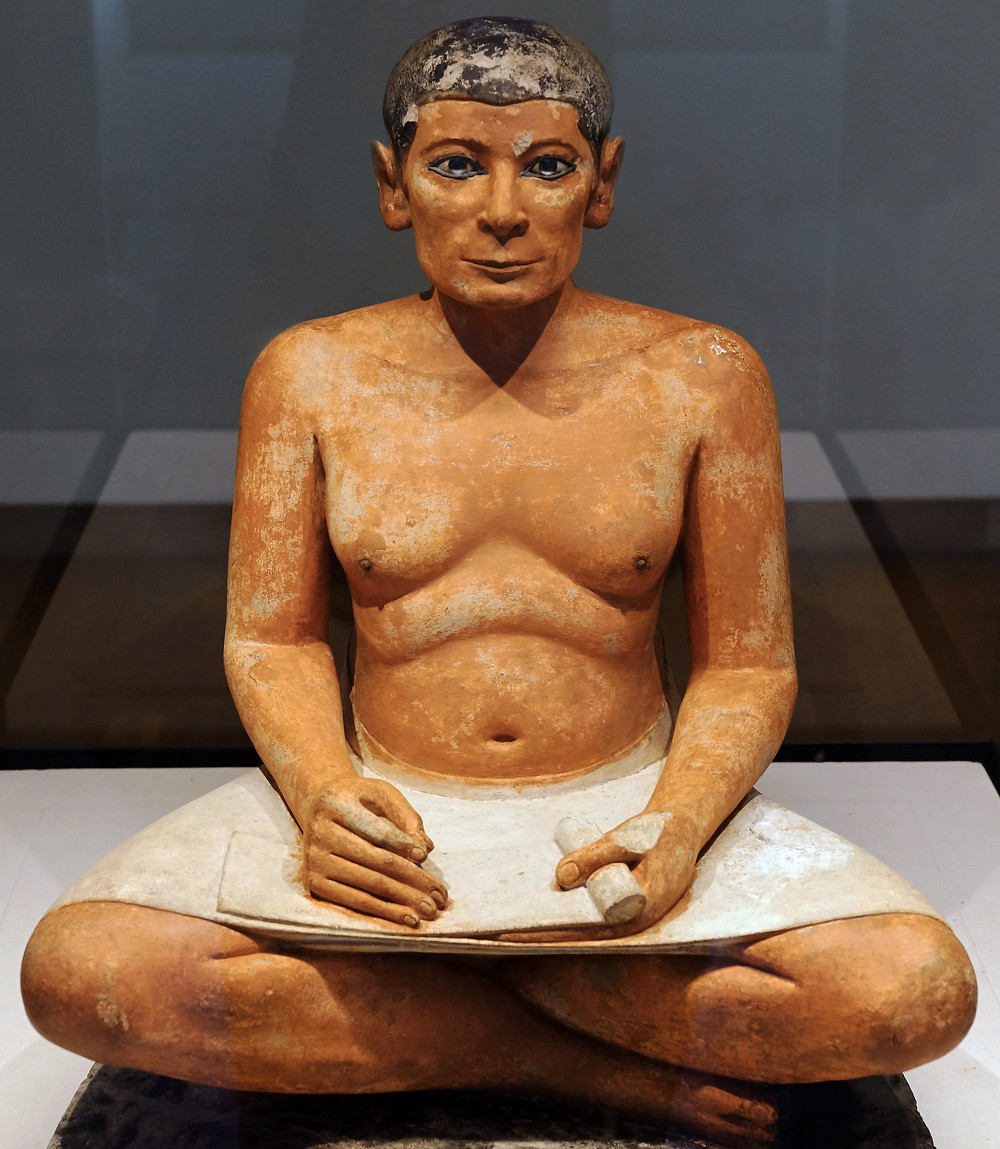

Seated Scribe, c. 2500 B.C.E., c. 4th Dynasty, Old Kingdom, painted limestone with rock crystal, magnesite, and copper/arsenic inlay for the eyes and wood for the nipples, found in Saqqara (photo: Steven Zucker, CC BY-NC-SA 2.0)
Most Egyptians followed the careers of their fathers and were taught by apprenticeship. Only the children of the higher classes, destined to become officials, were taught in schools and learned to read and write. Money in the modern sense did not exist in Egypt until the mid-fourth century B.C.E., so wages were usually paid in grain that could then be exchanged for copper or silver. Agriculture was the basis of the Egyptian economy and the foundation of the state, and produce was delivered to central storehouses to be administered and distributed.
Read essays about the various social strata in Egyptian society


Egyptian Social Organization: Administrative officials, priests, ranks of the military, and the general population
Read Now >/2 Completed
Art and Function
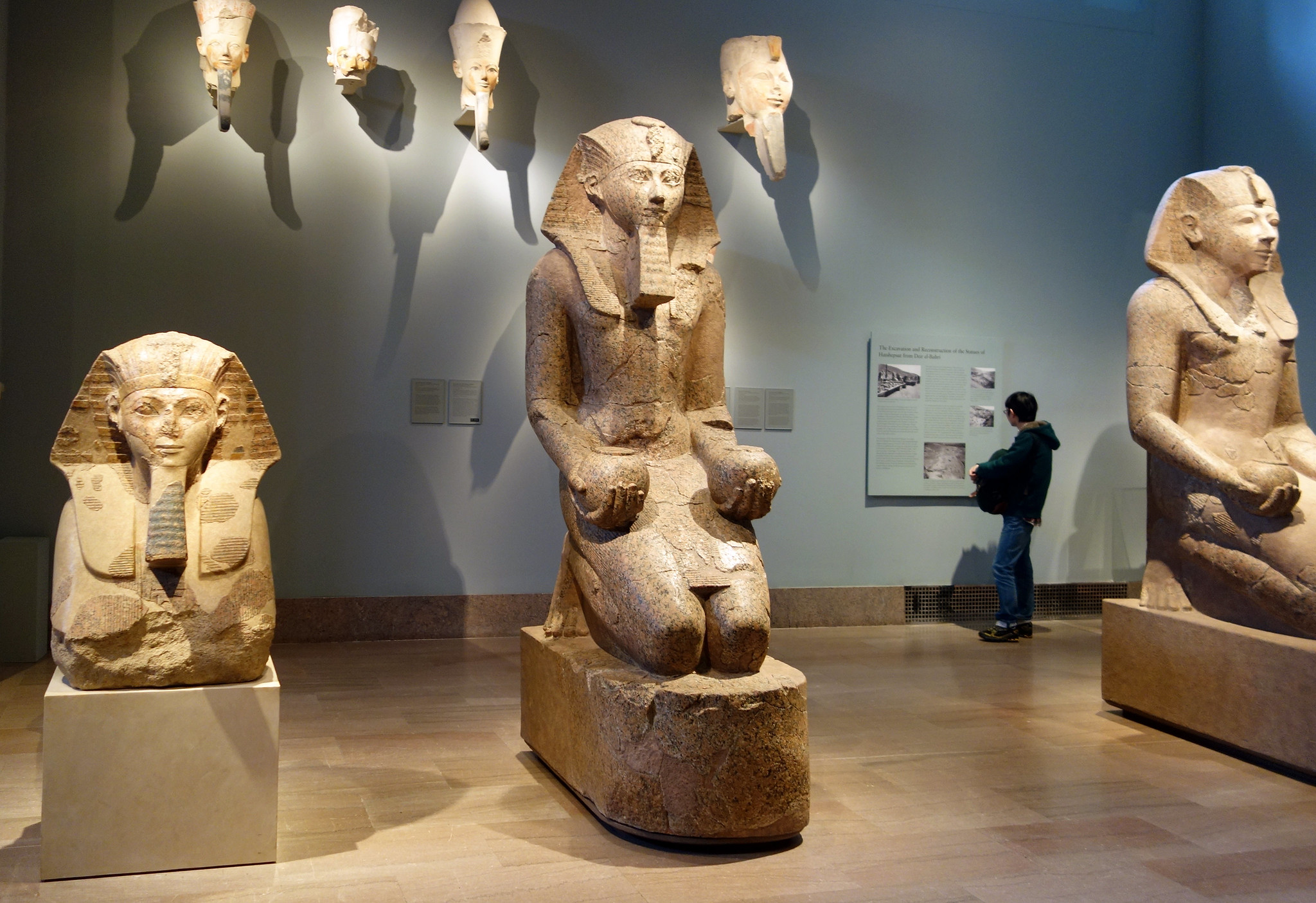

Large Kneeling Statue of Hatshepsut, c. 1479–1458 B.C.E., Dynasty 18, New Kingdom (Deir el-Bahri, Upper Egypt), granite, 261.5 x 80 x 137 cm (The Metropolitan Museum of Art)
Egyptian art is sometimes viewed as static and abstract when compared with the more naturalistic depictions of other cultures (ancient Greece for example). Much of Egyptian imagery—especially royal imagery—was governed by decorum (a sense of what was appropriate), and remained extraordinarily consistent throughout its long history. This is why their art may appear unchanging—and this was intentional. For the ancient Egyptians, consistency was a virtue and an expression of political stability, divine balance, and clear evidence of ma’at and the correctness of their culture. The Egyptians even had a tendency, especially after periods of disunion, towards archaism where the artistic style would revert to that of the earlier Old Kingdom which was perceived as a “golden age.”
Read essays about art and function
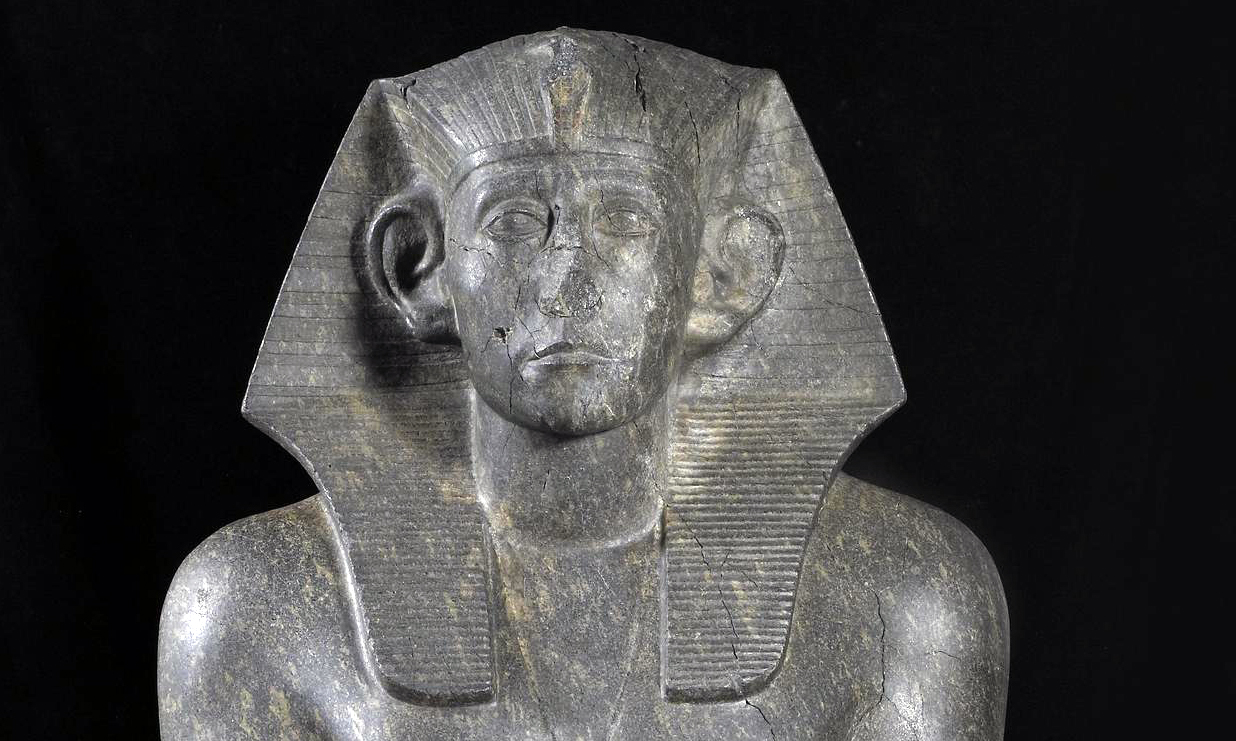
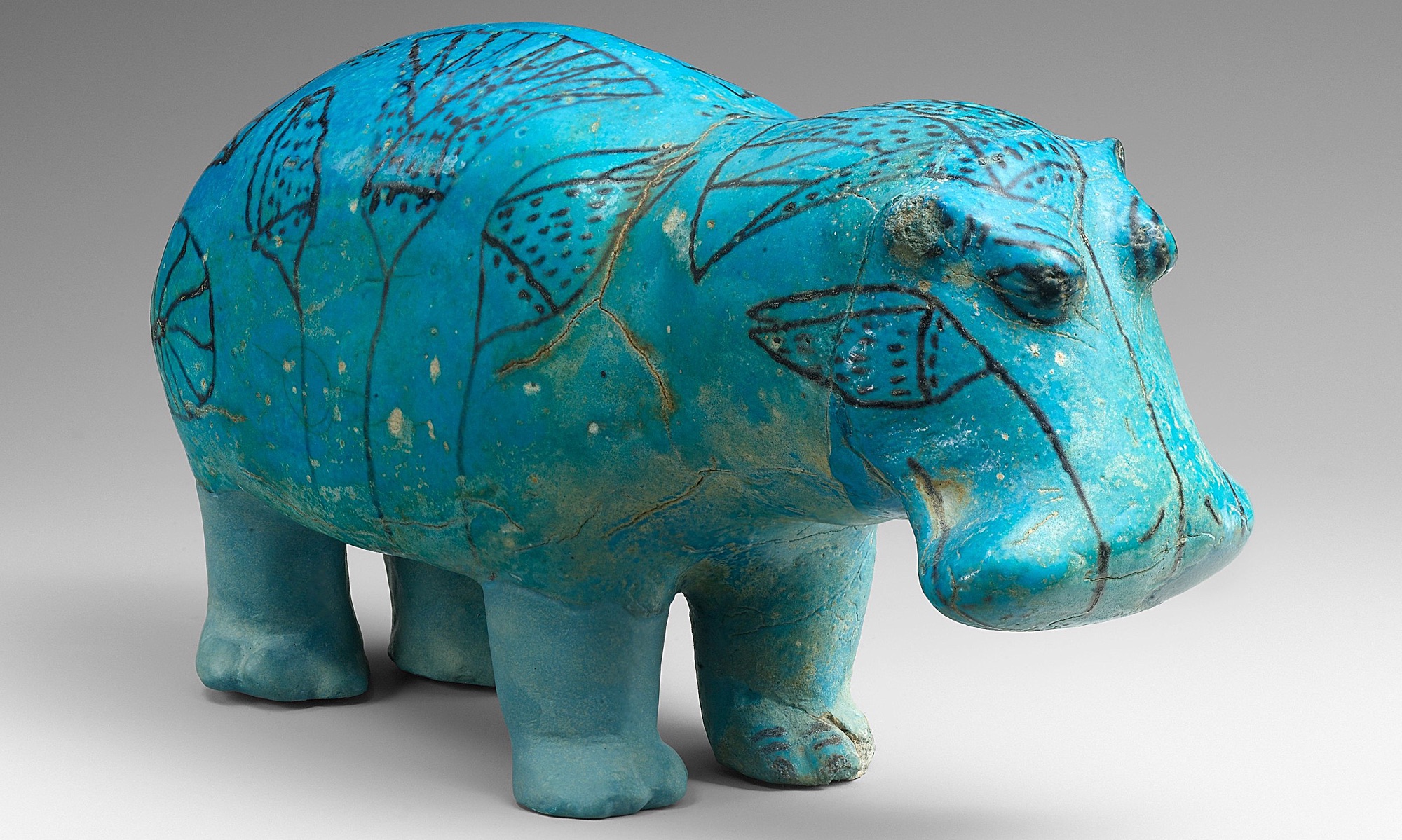


/2 Completed
Consistency and balance

The canon of proportions grid is clearly visible in the lower, unfinished register of the Stela of Userwer, and the use of hieratic scale (where the most important figures are largest) is evident the second register that shows Userwer, his wife and his parents seated and at a larger scale than the figures offering before them. Detail of the stela of the sculptor Userwer, 12th dynasty, limestone, from Egypt, 52 x 48 cm wide (© Trustees of the British Museum)
Consistency in representation was closely related to a fundamental belief that depictions had an impact beyond the image itself. This belief led to an active resistance to changes in codified depictions. Even the way that figures were planned and laid out by the artists was codified. During the Old Kingdom, the Egyptians developed a grid system, referred to as the canon of proportions, for creating systematic figures with the same proportions. Grid lines aligned with the top of the head, top of the shoulder, waist, hips, knees, and bottom of the foot (among other body joints).
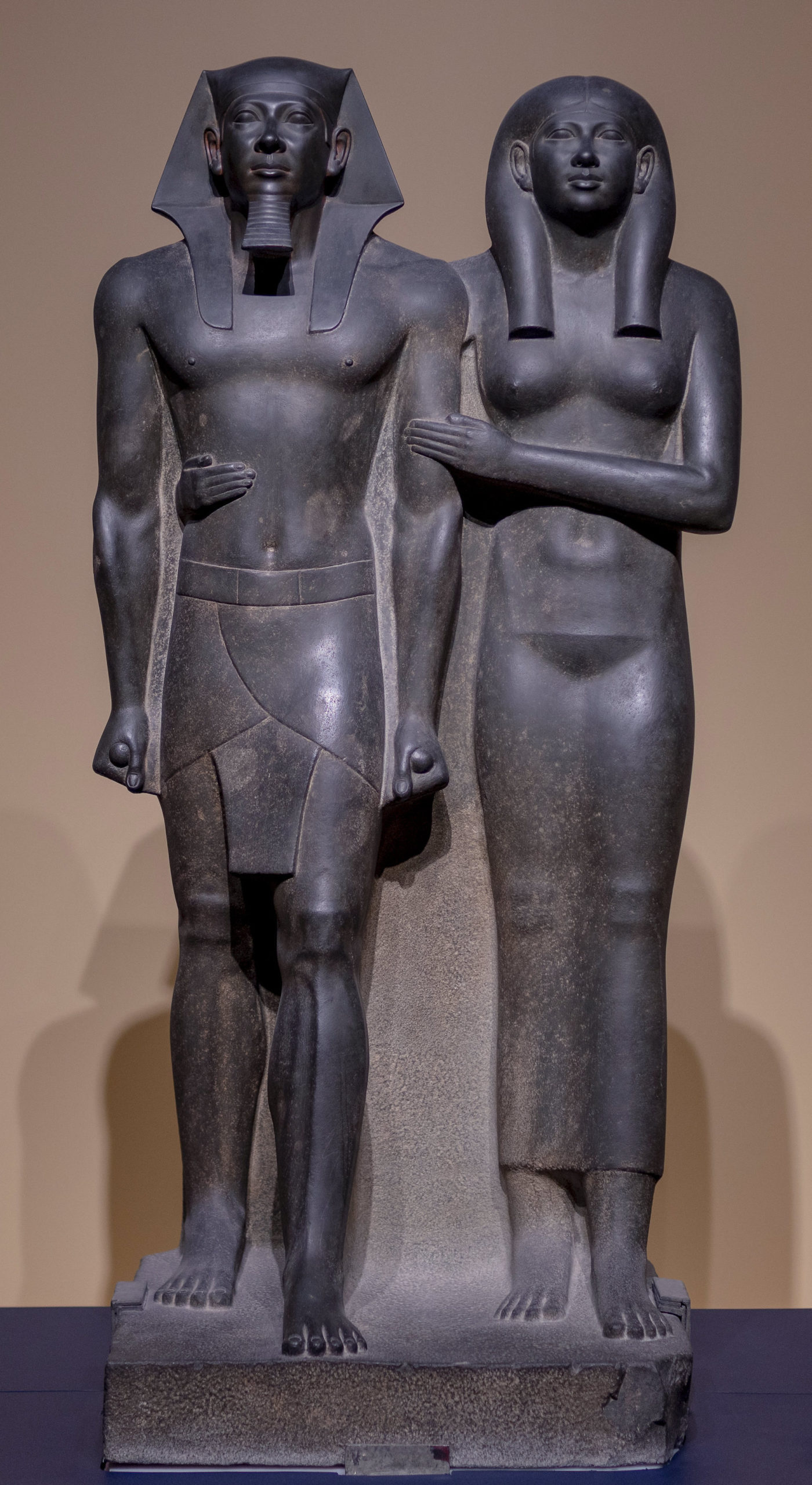

King Menkaura (Mycerinus) and Queen, 2490–2472 B.C.E., Old Kingdom, Dynasty 4, greywacke, Menkaura Valley Temple, Giza, Egypt, 142.2 x 57.1 x 55.2 cm, 676.8 kg (Museum of Fine Arts, Boston; photo: Steven Zucker, CC BY-NC-SA 2.0)
The grid aided the artist in ensuring that the proportions of their figures were correct, but those proportions shifted over time. For example, although 18 squares was the standard used for much of Egypt’s history, in the Amarna period 20 squares were used, resulting in figures with more elongated proportions.
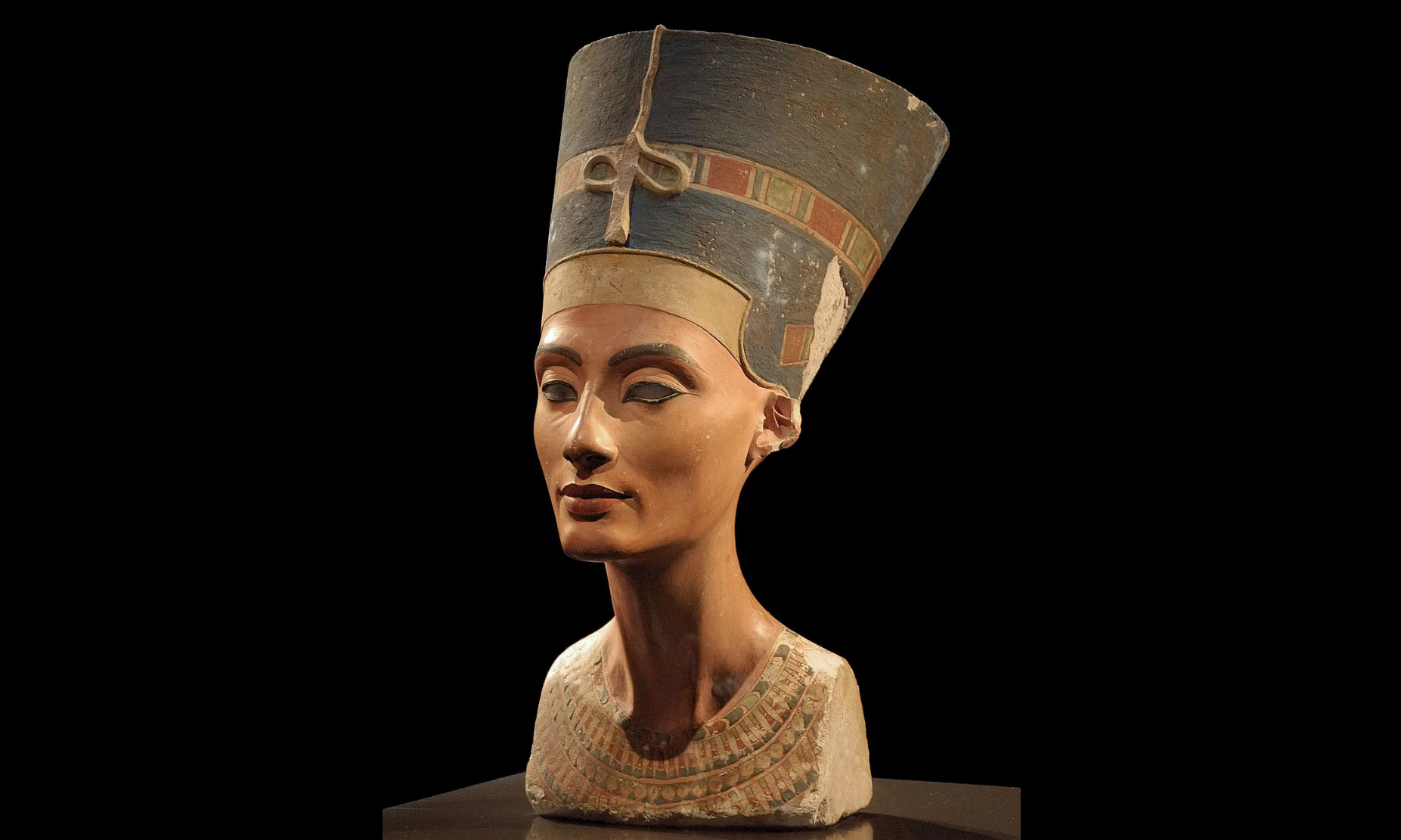

Thutmose, Model Bust of Queen Nefertiti, c. 1340 BCE, limestone and plaster, New Kingdom, 18th dynasty, Amarna Period (Egyptian Museum and Papyrus Collection/Neues Museum, Berlin)
Below are several examples of Egyptian art that demonstrate their primary stylistic characteristics. These include:
- the use of hierarchical scale
- the use of registers
- use of the canon of proportions (described above)
- a preference for balance
- the integration of perspectives.
Read essays and watch videos about consistency and balance

Stela of the sculptor Userwer: The lower part is still covered with the grid used for ensuring that the proportions of the figures were correct.
Read Now >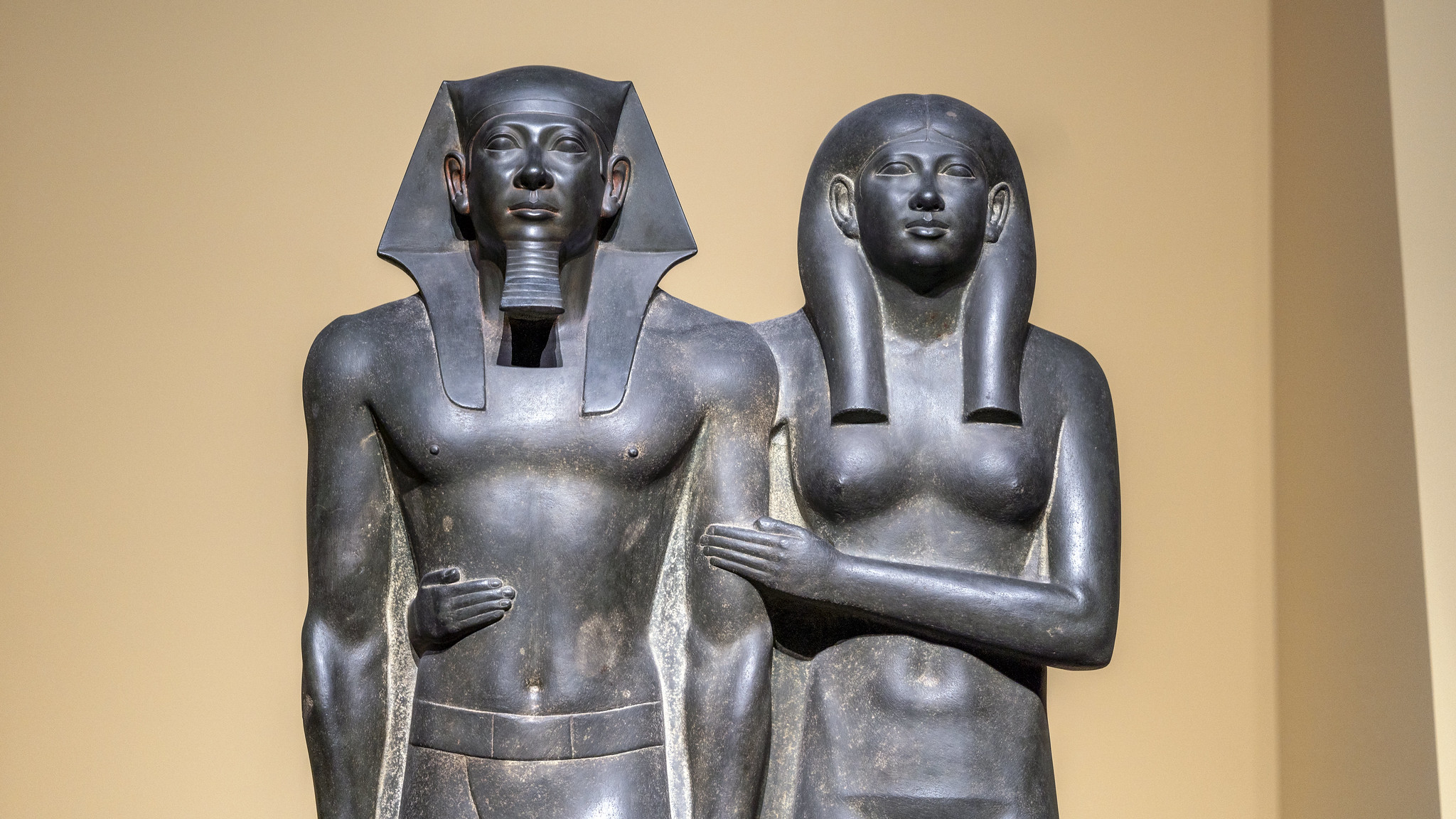
King Menkaure (Mycerinus) and queen: They both look beyond the present and into timeless eternity, their otherworldly visage displaying no human emotion whatsoever.
Read Now >
Thutmose, Model Bust of Queen Nefertiti: This stunning bust exemplifies a change in style.
Read Now >
/4 Completed
Creative details
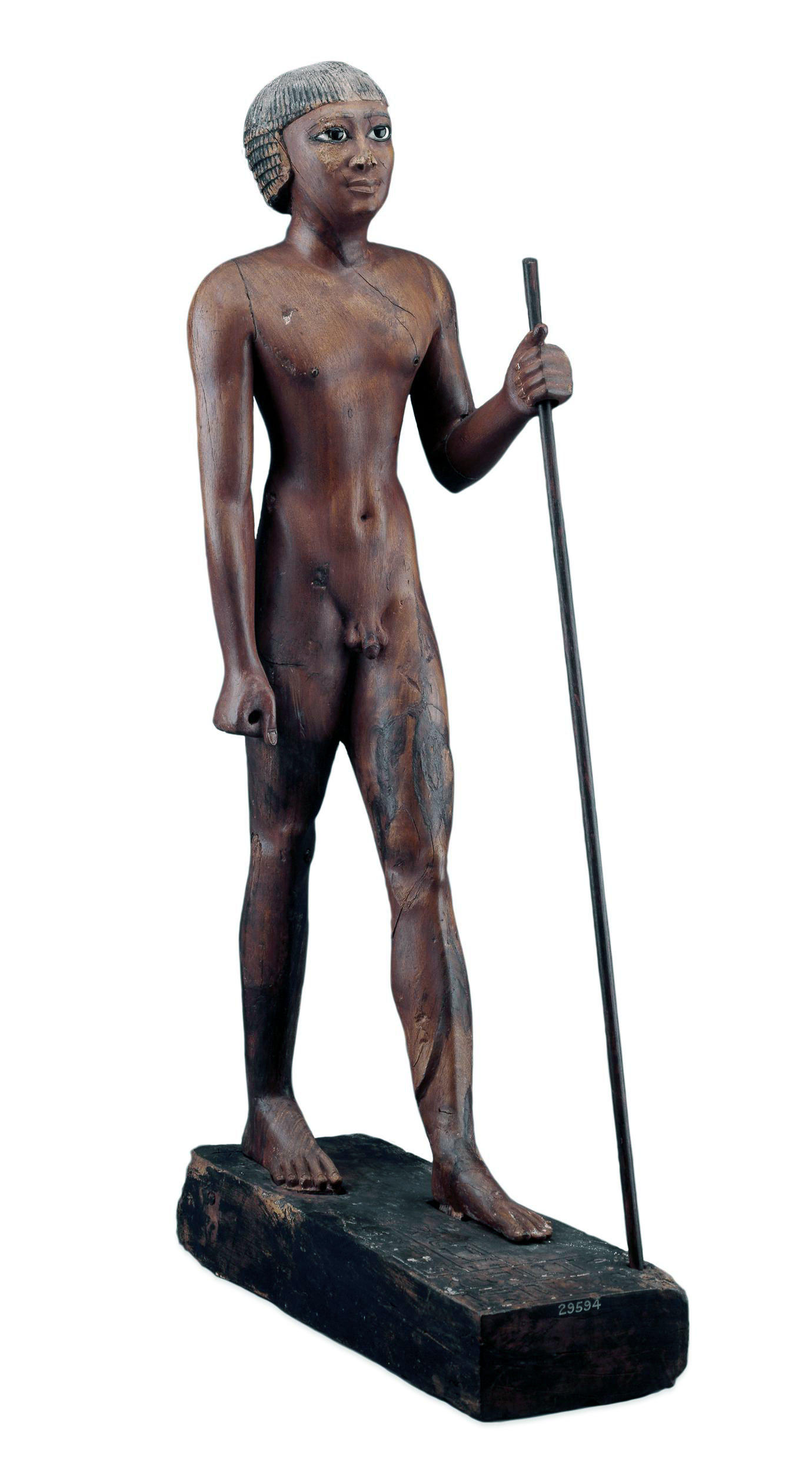

Nude figure of the Seal Bearer Tjetji, 2321 B.C.E.–2184 B.C.E. (6th Dynasty), from Akhmim, Upper Egypt, wood, obsidian, limestone, and copper, 75 cm high (© Trustees of the British Museum)
Although much Egyptian art is formal, many surviving examples of highly expressive depictions full of creative details prove that the ancient Egyptian artists were fully capable of naturalistic representations. Note, for example, the sensitive modeling of the musculature and close attention paid to realistic physical detail evident in a wood statue of a high official (the Seal Bearer Tjetji) from a Late Old Kingdom tomb. These very unusual and enigmatic statuettes of nude high officials, which are depicted in a standard pose of striding forward with left leg advanced and holding a long staff, were often painted and had eyes of inlaid stone set in copper.
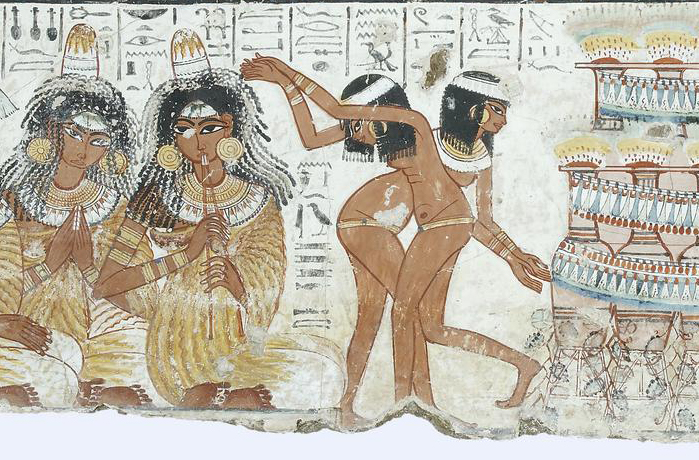

Musicians and dancers (detail), A feast for Nebamun, Tomb-chapel of Nebamun, c. 1350 B.C.E., 18th Dynasty, paint on plaster, whole fragment: 88 x 119 cm, Thebes © Trustees of the British Museum
Nebamun’s tomb, with its spectacular paintings, includes several examples that demonstrate a careful observation of the natural world—especially notable in the energetic hunting cat and the sinuous dancing of the entertainers at the banquet. A marvelous wooden head of Queen Tiye presents a woman of strong personality with details that hint at her formidable character.
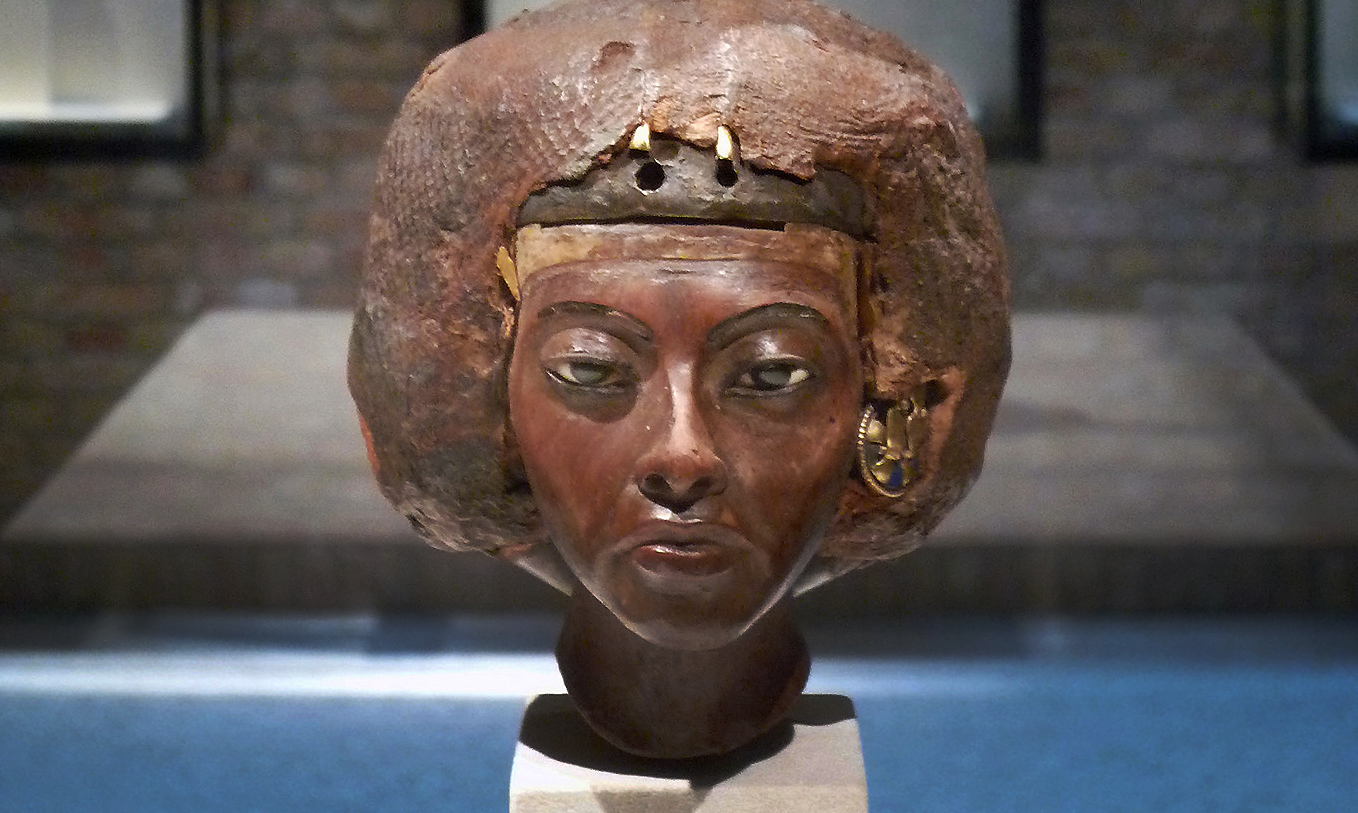

Portrait Head of Queen Tiye with a Crown of Two Feathers, c. 1355 B.C.E., Amarna Period, Dynasty 18, New Kingdom, Egypt, yew wood, lapis lazuli, silver, gold, faience, 22.5 cm high (Egyptian Museum and Papyrus Collection at the Neues Museum, Berlin)
Read essays about creative details
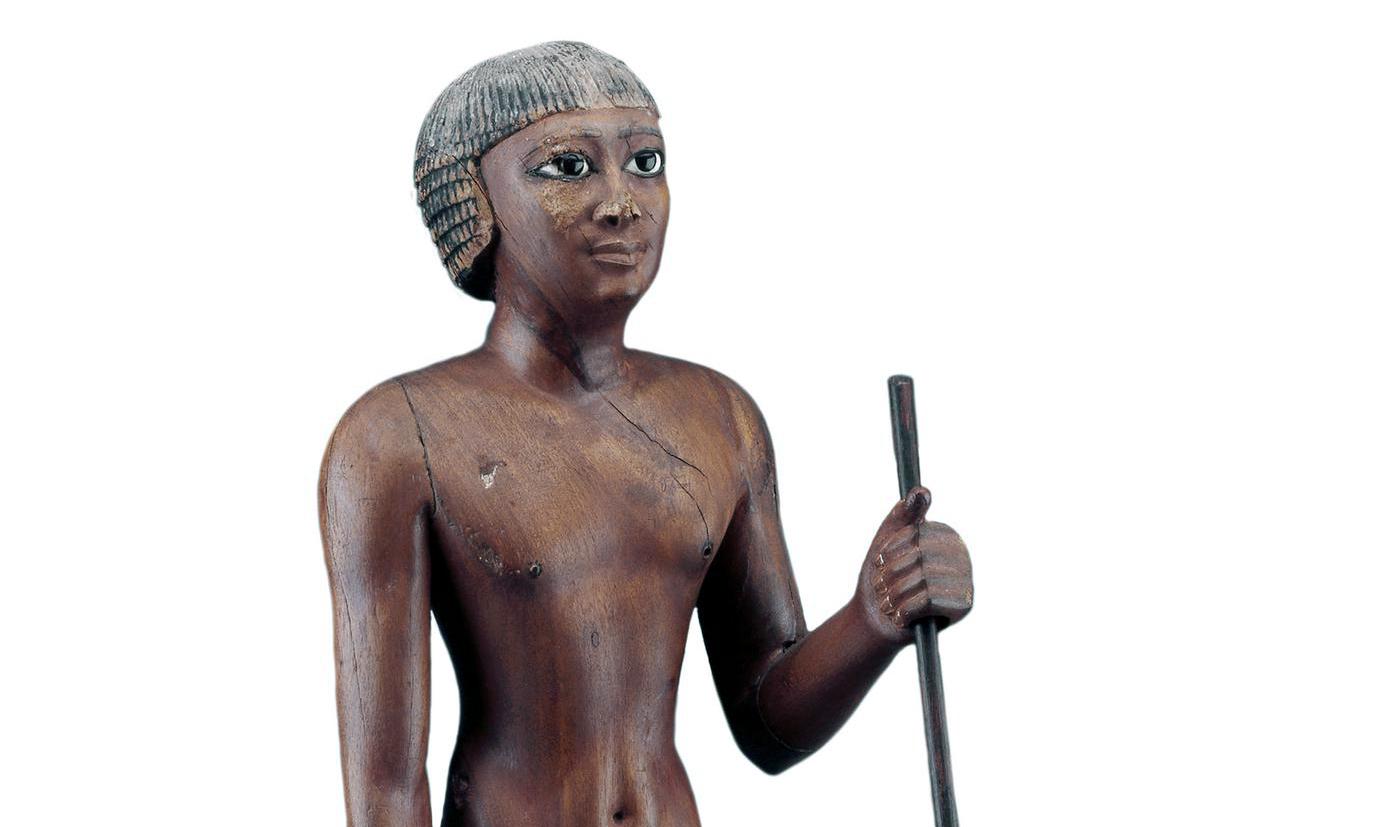

Wooden tomb statue of Tjeti: The sculptor of this example has carefully modeled the muscles on the torso and legs, and paid close attention to the detail of the face.
Read Now >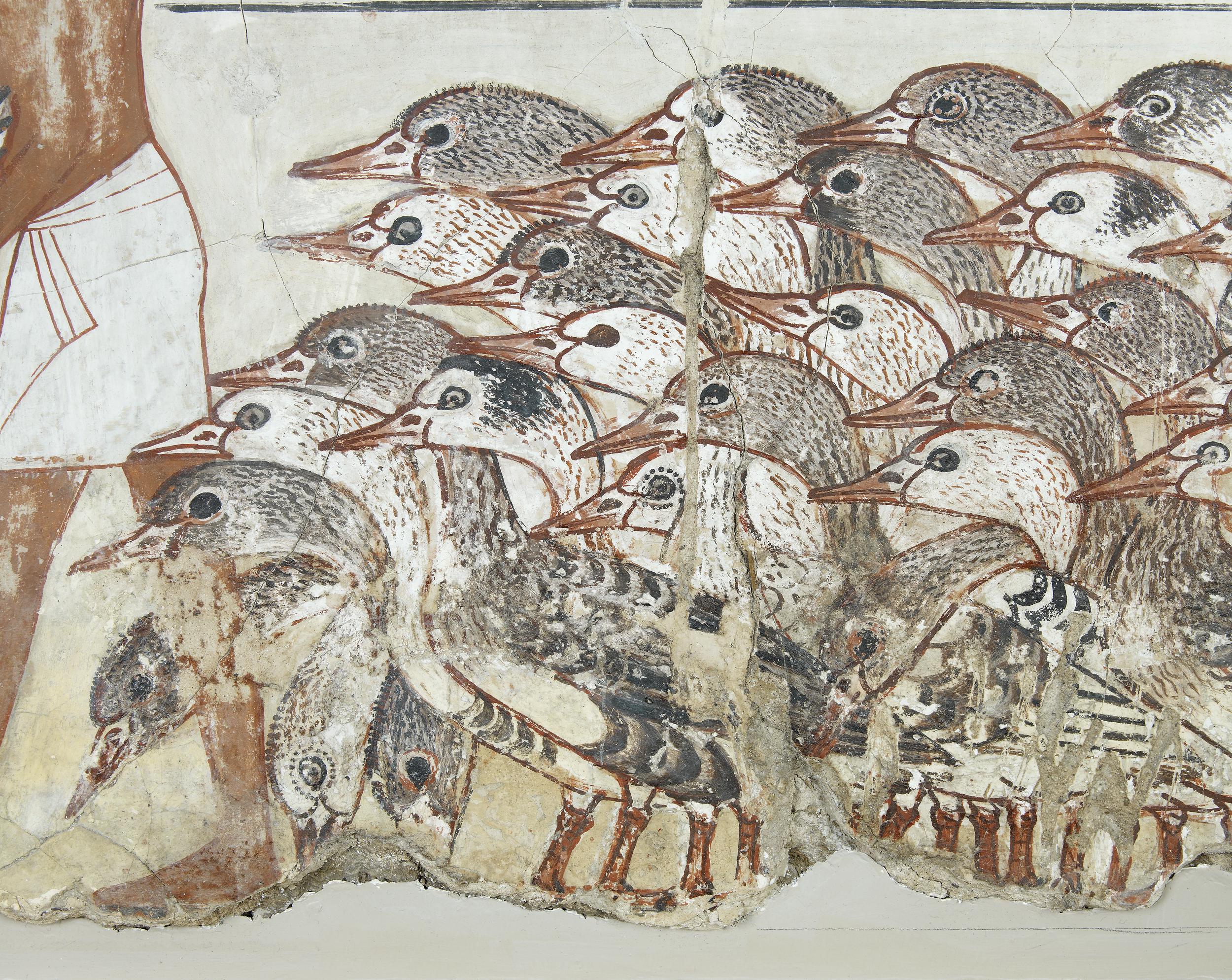
Paintings from the Tomb-chapel of Nebamun: He is shown hunting birds from a small boat in the marshes of the Nile with his wife Hatshepsut and their young daughter.
Read Now >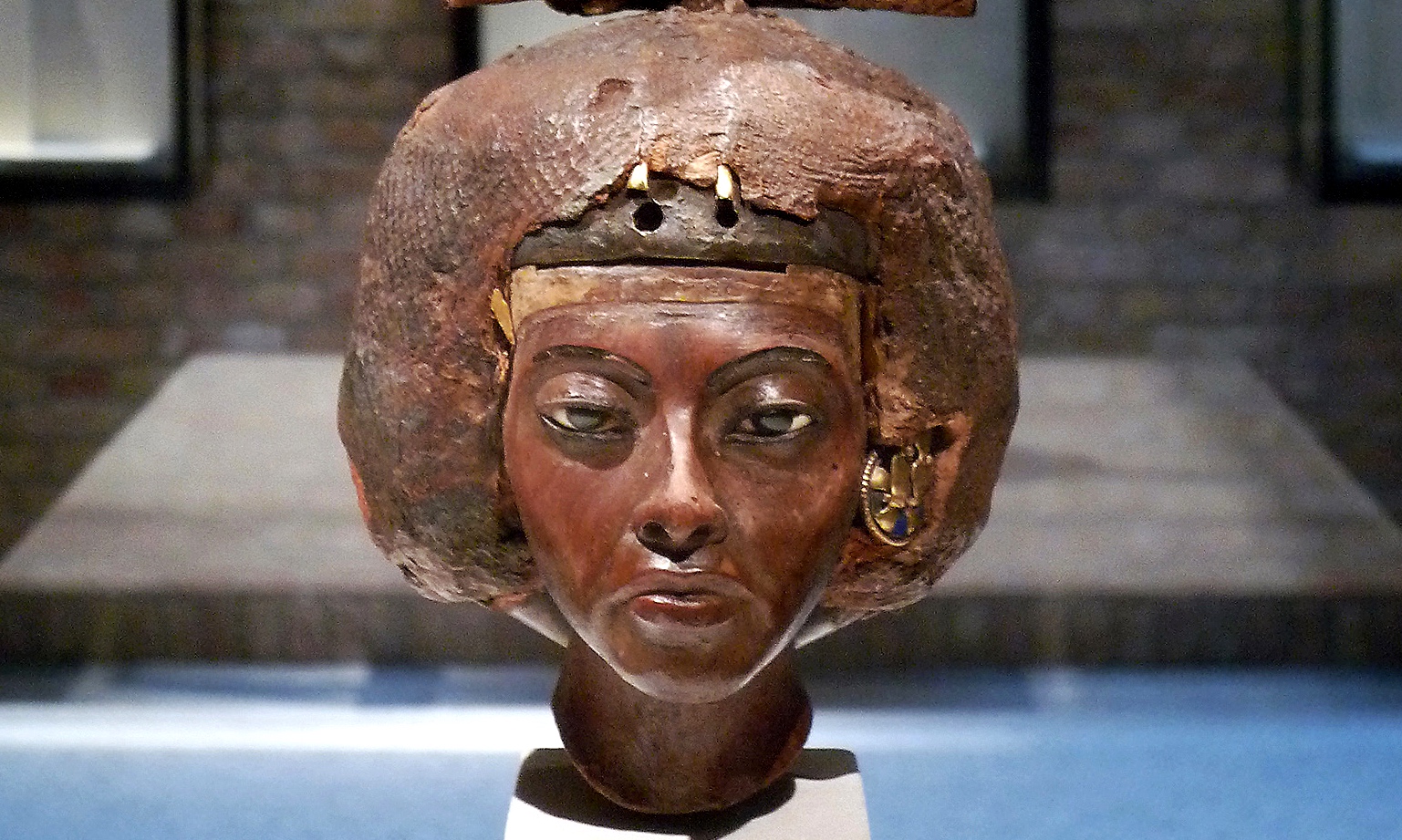
Portrait Head of Queen Tiye: She was a powerful figure, but her royal life was complicated, as demonstrated through this changing statue.
Read Now >/3 Completed
Metalworking Traditions
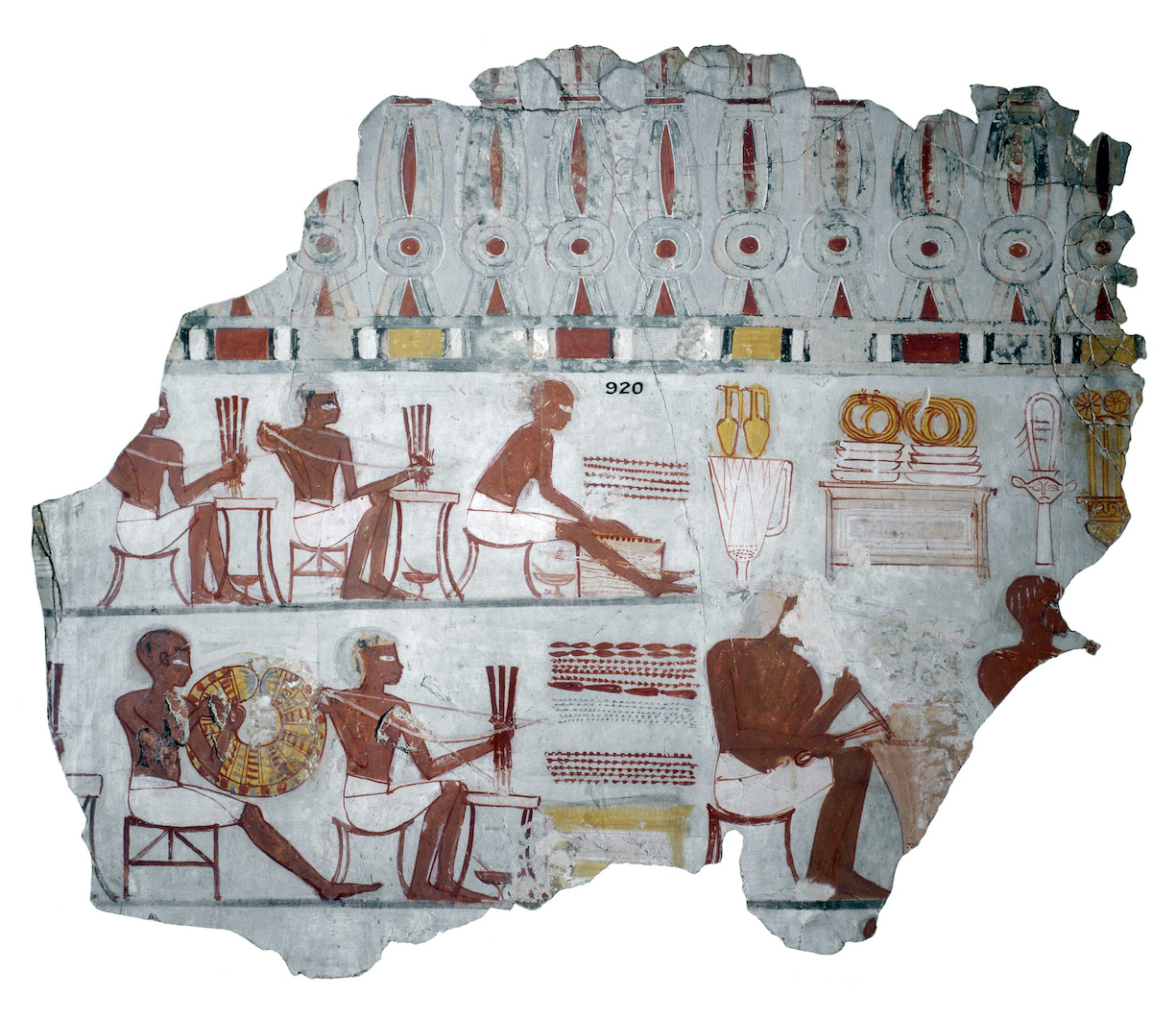

Scene showing the manufacture of valuable items, such as jewelry. Wall-painting, probably from the tomb of Sobekhotep, Thebes, c. 1400 B.C.E., New Kingdom, reign of Thutmose IV, painted stucco, 60 x 58.5 (© Trustees of the British Museum)
Egyptian artisans were highly skilled metalworkers from early times; although few metal sculptures have survived, those that are preserved show an incredible level of technical achievement. As with other types of craft, like woodworking, preserved images of artisans in their workshops found in private tombs provide information about the processes of production For instance, we can see a group of jewelers at work in a painting from the tomb of Sebekhotep.

Pectoral and Necklace of Sithathoryunet with the Name of Senwosret II, Middle Kingdom, Dynasty 12, reign of Senwosret II, c. 1887–1878 B.C.E., Egypt, Fayum Entrance Area, el-Lahun (Illahun, Kahun; Ptolemais Hormos), Tomb of Sithathoryunet (BSA Tomb 8), EES 1914, Gold, carnelian, feldspar, garnet, turquoise, lapis lazuli
The most beautifully crafted pieces of jewelry display elegant designs, incredible intricacy, and astonishingly precise stone-cutting and inlay, reaching a level that modern jewelers would be hard-pressed to achieve. The jewelry of a Middle Kingdom princess, found in her tomb at el-Lahun in the Fayum region is one spectacular example.
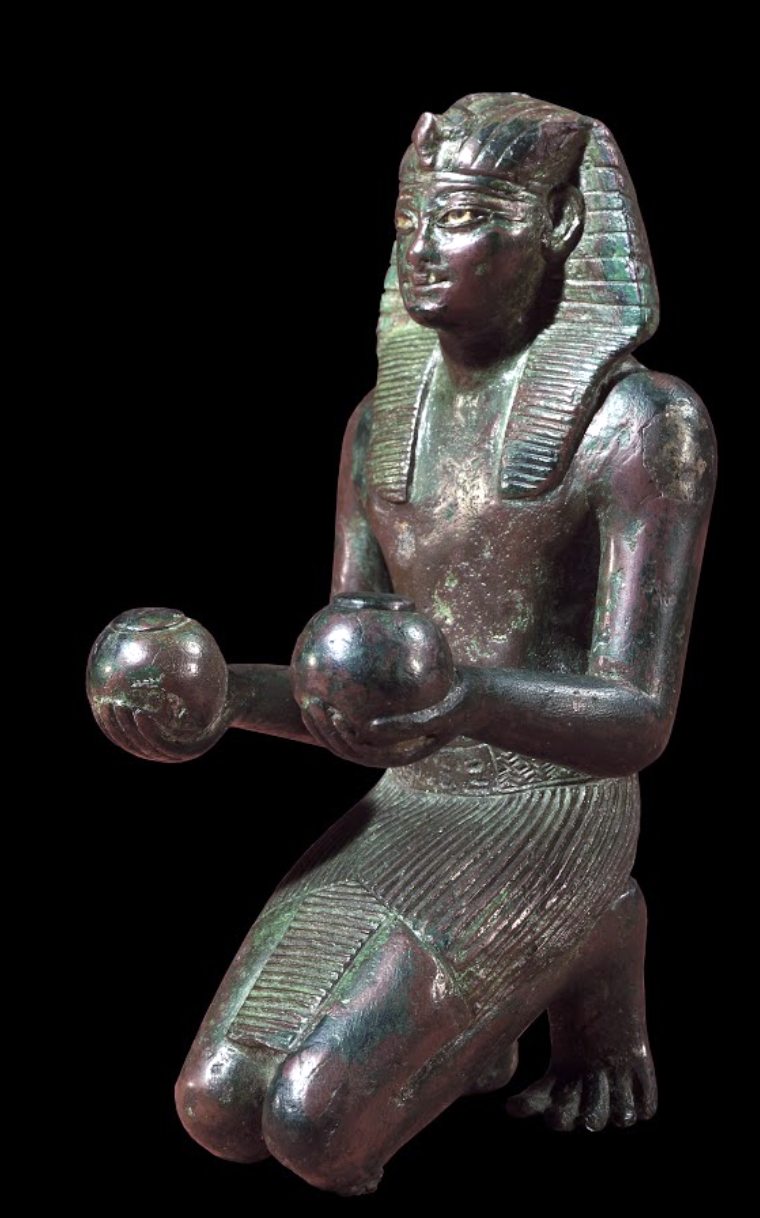

Statuette of Thutmose IV, 1400–1390 B.C.E., 19th Dynasty, ancient Egypt, bronze, silver, calcite, 14.7 x 6.4 cm (© Trustees of the British Museum)
The metal statues that survive demonstrate a high level of skill in both sheet working/metal forming and casting in copper and bronze. This marvelous hollow-cast bronze statuette of a kneeling Thutmosis IV, presenting an offering of wine, provides a peek into the abilities of Egypt’s craftsmen. Note that the arms were created separately and joined to the body on tenons and the eyes were originally inlaid.
Read essays and watch a video about metalworking traditions


Pectoral and necklace of Sithathoryunet: Fashioned delicately in gold, carnelian, feldspar, garnet, turquoise, and lapis lazuli.
Read Now >
Bronze statuette of Thutmose IV: Very few metal statues survive that date from before the Late Period, though the Egyptians did have the technology to make large copper statues as early as the Old Kingdom.
Read Now >/3 Completed
This brief glimpse at the world of ancient Egypt is just a springboard for gaining an understanding of this compelling and complex culture.
A final note
The wonder of the internet is the astonishing access to information; one of the big problems with the internet is that anyone, regardless of knowledge or training, can post whatever they like and that information is presented at the same level as content put out by the experienced and trained. Information about ancient Egypt should always come from a well-vetted source, as there is a great deal of misinformation. The culture is astonishing enough on its own. Egypt remains highly influential across different areas of culture and vast swaths of time and space—Egyptian glass beads have been excavated in Viking tombs and revivals of Egyptian style still happen on an almost cyclical basis, even millenia later. We are surrounded by Egyptian imagery and concepts even if we don’t realize it; those emojis we use with such abandon are decidedly hieroglyphic. The more we know about what came before, the better we can grasp everything that has happened since. Only by understanding the past can we really envision the possibilities of the present and plan for the future.
Key questions to guide your reading
How did the annual flooding of the Nile help form the Egyptian view of the world?
How might the regular behavior of certain animals—like falcons, vultures, snakes, and scarab beetles— suggest "heavenly wisdom" to the careful observer?
How would you want to be depicted for eternity? What identifying symbols would you want to include?
Jump down to Terms to KnowHow did the annual flooding of the Nile help form the Egyptian view of the world?
How might the regular behavior of certain animals—like falcons, vultures, snakes, and scarab beetles— suggest "heavenly wisdom" to the careful observer?
How would you want to be depicted for eternity? What identifying symbols would you want to include?
Jump down to Terms to KnowTerms to know and use
hieroglyph
ma'at
dynastic
pharaoh
theocracy
faience
canon of proportions
hierarchical scale
Nile River
Learn more
Need teaching images? Here is a Google Slideshow with many of the primary images in this chapter
Read a chapter about Ancient Egyptian religious life and afterlife

