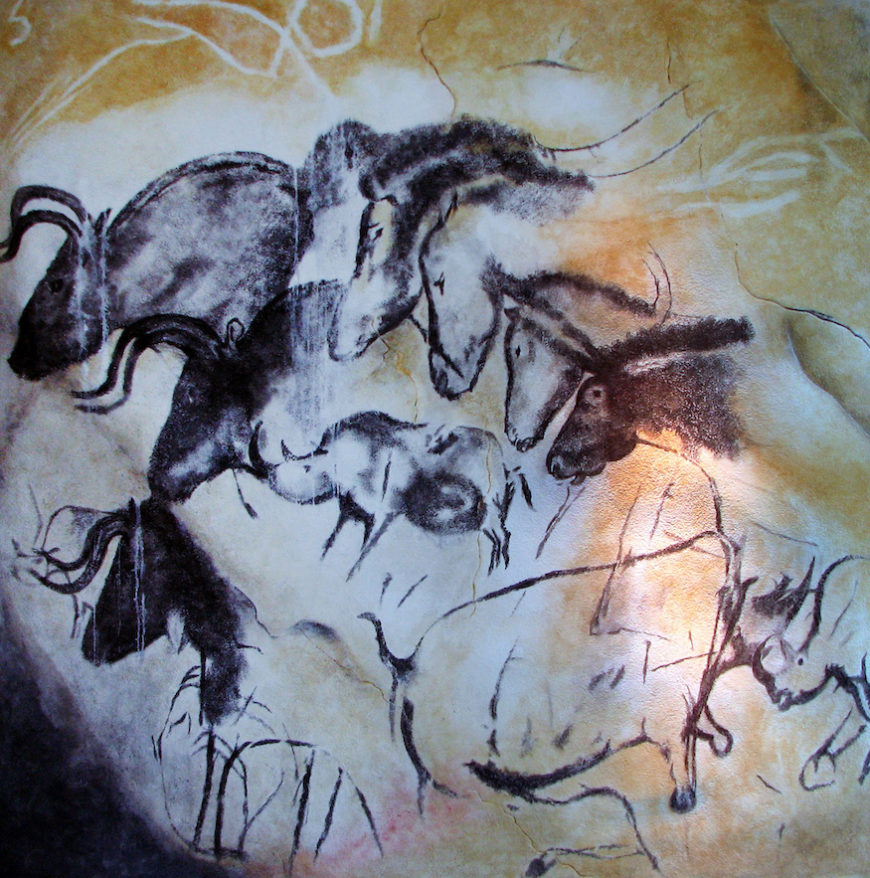
Replica of the painting from the Chauvet-Pont-d’Arc Cave in southern France (Anthropos museum, Brno)
The oldest art: ornamentation
Humans (Homo sapiens) make art. We do this for many reasons and with whatever technologies are available to us. Recent research suggests that Neanderthals also made art.
Extremely old, non-representational ornamentation has been found across Africa. The oldest firmly-dated example is a collection of 82,000 year old Nassarius snail shells found in Morocco that are pierced and covered with red ochre. Wear patterns suggest that they may have been strung beads. Nassarius shell beads found in Israel may be more than 100,000 years old and in the Blombos cave in South Africa, pierced shells and small pieces of ochre (red Hematite) etched with simple geometric patterns have been found in a 75,000-year-old layer of sediment.
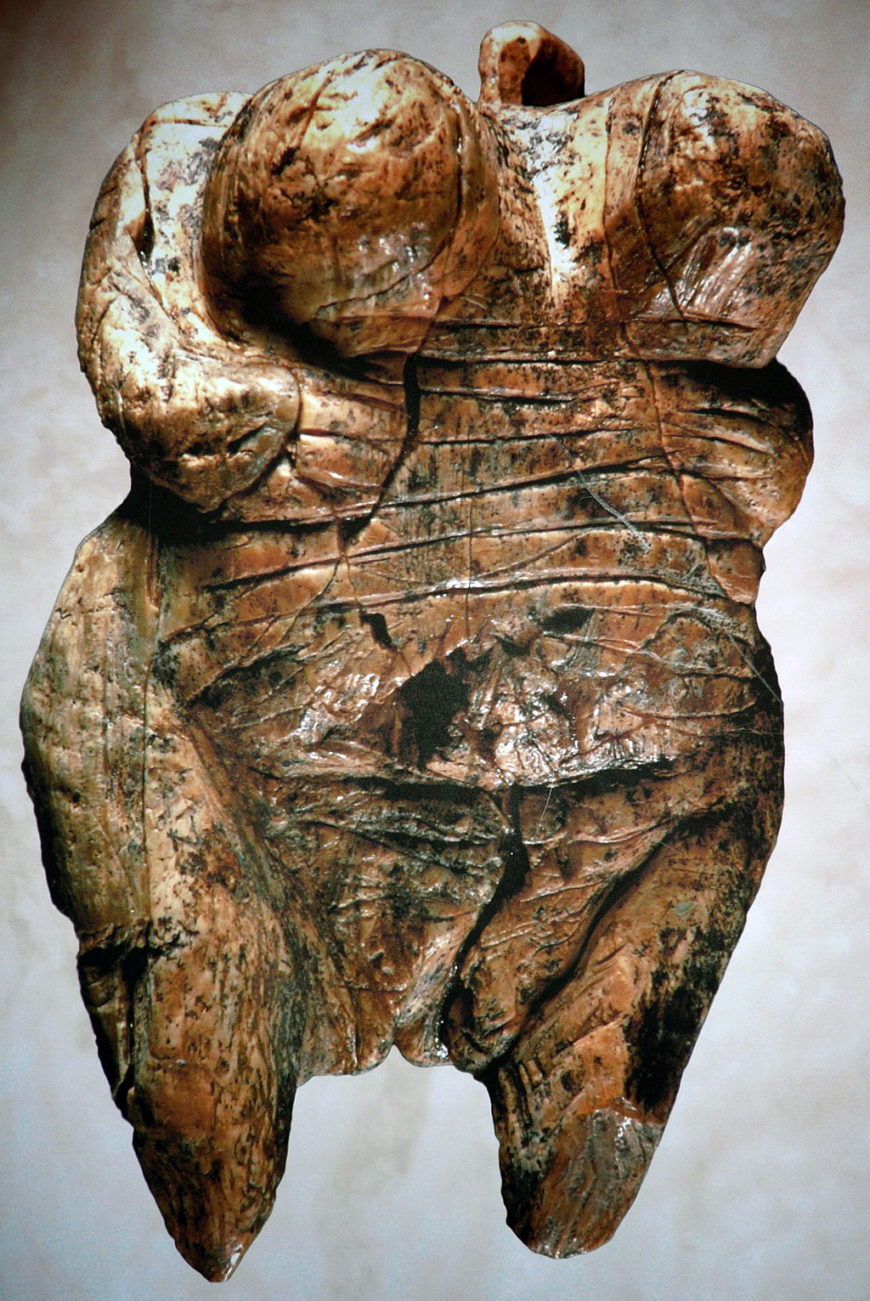

Female Figure of Hohlefels, c. 35,000 B.C.E., ivory, found in cave near Schelklinge, southern Germany (photo: Ramessos, CC BY-SA 3.0)
The oldest representational art
Some of the oldest known representational imagery comes from the Aurignacian culture of the Upper Paleolithic period (Paleolithic means old stone age). Archaeological discoveries across a broad swath of Europe (especially Southern France, Northern Spain, and Swabia, in Germany) include over two hundred caves with spectacular Aurignacian paintings, drawings, and sculpture that are among the earliest undisputed examples of representational image-making. Among the oldest of these is a 2.4-inch tall female figure carved out of mammoth ivory that was found in six fragments in the Hohle Fels cave near Schelklingen in southern Germany. It dates to 35,000 B.C.E.
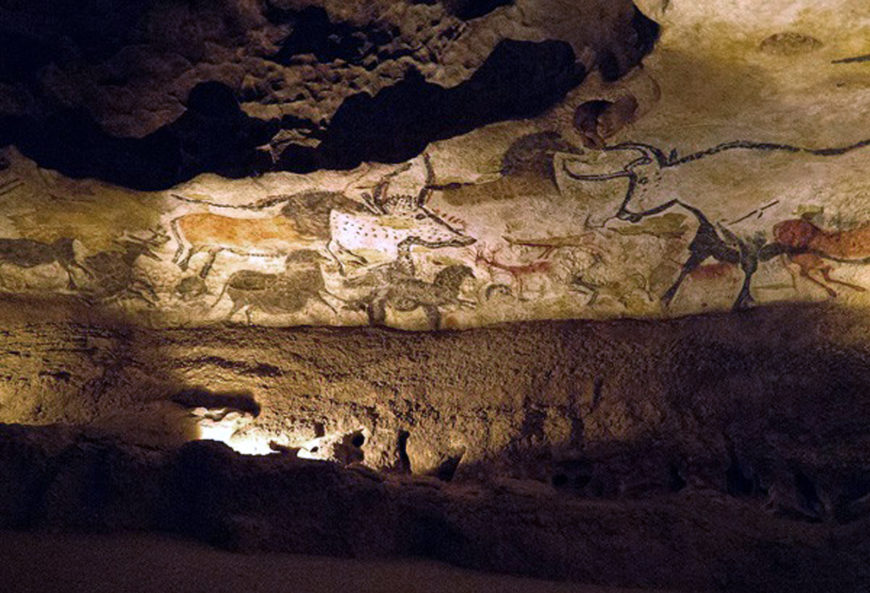

Left wall of the Hall of Bulls, Lascaux II (replica of the original cave, which is closed to the public), original cave: c. 16,000–14,000 B.C.E., 11 feet 6 inches long
The caves
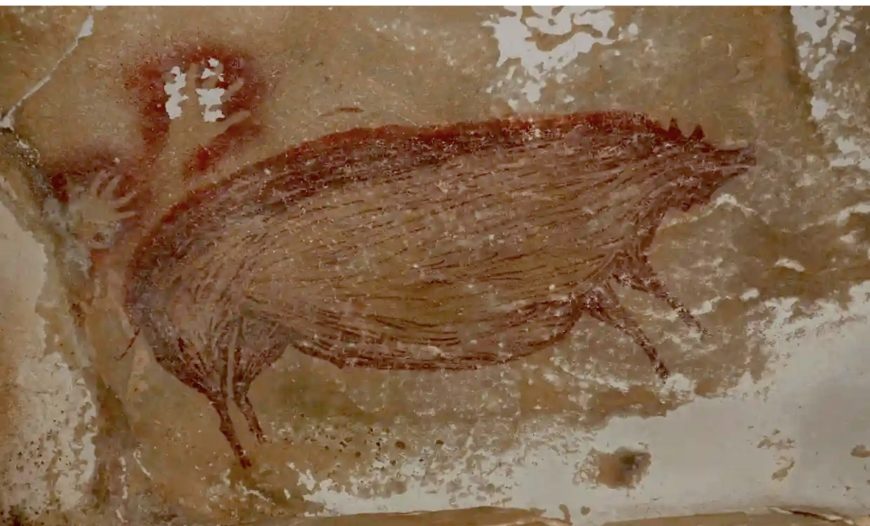
Warty pig (Sus celebensis), c. 43,900 B.C.E., painted with ocher (clay pigment), Maros-Pangkep caves, Leang Bulu’ Sipong 4, South Sulawesi, Indonesia
The caves at Chauvet-Pont-d’Arc, Lascaux, Pech Merle, and Altamira contain the best known examples of pre-historic painting and drawing. Here are remarkably evocative renderings of animals and some humans that employ a complex mix of naturalism and abstraction. Archaeologists that study Paleolithic era humans, believe that the paintings discovered in 1994, in the cave at Chauvet-Pont-d’Arc in the Ardéche valley in France, are more than 30,000 years old. The images found at Lascaux and Altamira are more recent, dating to approximately 15,000 B.C.E. The paintings at Pech Merle date to both 25,000 and 15,000 B.C.E. The world’s oldest known cave painting was found in Sulawesi, Indonesia in 2017 and was made at least 45,500 years ago.
What can we really know about the creators of these paintings and what the images originally meant? These are questions that are difficult enough when we study art made only 500 years ago. It is much more perilous to assert meaning for the art of people who shared our anatomy but had not yet developed the cultures or linguistic structures that shaped who we have become. Do the tools of art history even apply? Here is evidence of a visual language that collapses the more than 1,000 generations that separate us, but we must be cautious. This is especially so if we want to understand the people that made this art as a way to understand ourselves. The desire to speculate based on what we see and the physical evidence of the caves is wildly seductive.
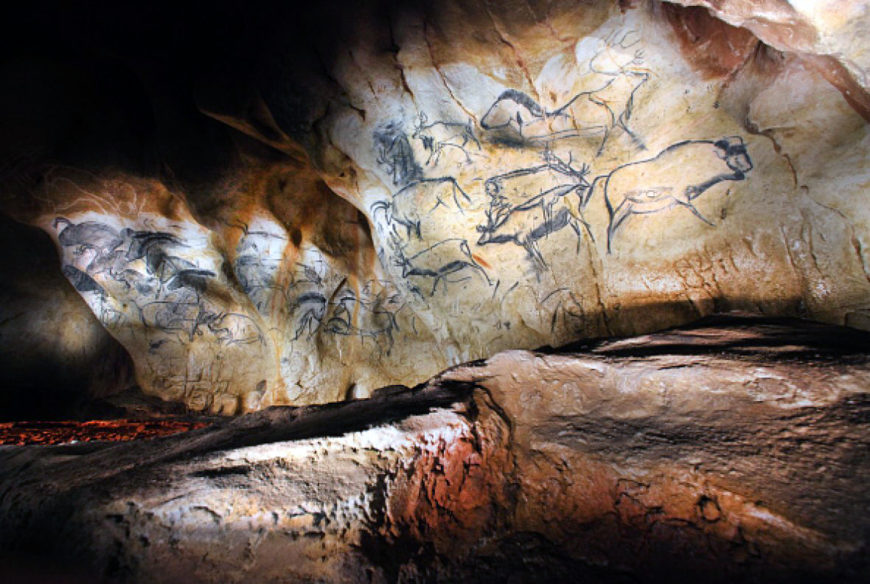
Chauvet-Pont-d’Arc
The cave at Chauvet-Pont-d’Arc is over 1,000 feet in length with two large chambers. Carbon samples date the charcoal used to depict the two head-to-head Rhinoceroses (see the image above, bottom right) to between 30,340 and 32,410 years before 1995 when the samples were taken. The cave’s drawings depict other large animals including horses, mammoths, musk ox, ibex, reindeer, aurochs, megaceros deer, panther, and owl (scholars note that these animals were not then a normal part of people’s diet). Photographs show that the drawing at the top of this essay is very carefully rendered but may be misleading. We see a group of horses, rhinos, and bison and we see them as a group, overlapping and skewed in scale. But the photograph distorts the way these animal figures would have been originally seen. The bright electric lights used by the photographer create a broad flat scope of vision; how different to see each animal emerge from the dark under the flickering light cast by a flame.
In a 2009 presentation at University of California San Diego, Dr. Randell White, Professor of Anthropology at New York University, suggested that the overlapping horses pictured above might represent the same horse over time, running, eating, sleeping, etc. Perhaps these are far more sophisticated representations than we have imagined. There is another drawing at Chauvet-Pont-d’Arc that cautions us against ready assumptions. It has been interpreted as depicting the thighs and genitals of a woman but there is also a drawing of a bison and a lion, and the images are nearly intertwined. In addition to the drawings, the cave is littered with the skulls and bones of cave bear and the track of a wolf. There is also a footprint thought to have been made by an eight-year-old boy.
Clovis culture
Although the Paleo-Indians who migrated to America from Asia (across the Bering Strait — a land bridge that once joined present-day Alaska and eastern Siberia) during the Pleistocene Epoch (Ice Age) did not leave behind a written (or even a large material) record, they can be identified by specific toolkits. Clovis points, for example, reveal technologies of hunting and processing meat, as well as crafting a sharp point from available resources. Workers used a hard rock to chip flakes from a softer one, shaping it into a sturdy point that could be used by hand or fastened to a wooden spear.

Clovis points from the Rummells-Maske site, Cedar County, Iowa (photo: Billwhittaker, CC BY-SA 3.0)
These tools reveal that Clovis people were hunter-gatherers, relying upon big game. As ice thawed, toolkits diversified. Later Archaic people left behind wooden fishing spears reflecting an expansion of hunting and diet, possible boat technology, and a variety of specialized stone tools. But the most significant development in the Americas was the start of agriculture which fundamentally altered lifestyles of people throughout the hemisphere.
Additional resources
Is this cave painting humanity’s oldest story?
U-Th dating of carbonate crusts reveals Neandertal origin of Iberian cave art
Neanderthal artists made oldest-known cave paintings
World’s oldest known cave painting found in Indonesia
Pig Painting May Be World’s Oldest Cave Art Yet, Archaeologists Say
The cave of Chauvet-Pont-d’Arc
Lascaux on The Metropolitan Museum of Art’s Heilbrunn Timeline of Art History
For instructors: related lesson plan on Art History Teaching Resources
Smarthistory images for teaching and learning:
[flickr_tags user_id=”82032880@N00″ tags=”Willendorf,”]


