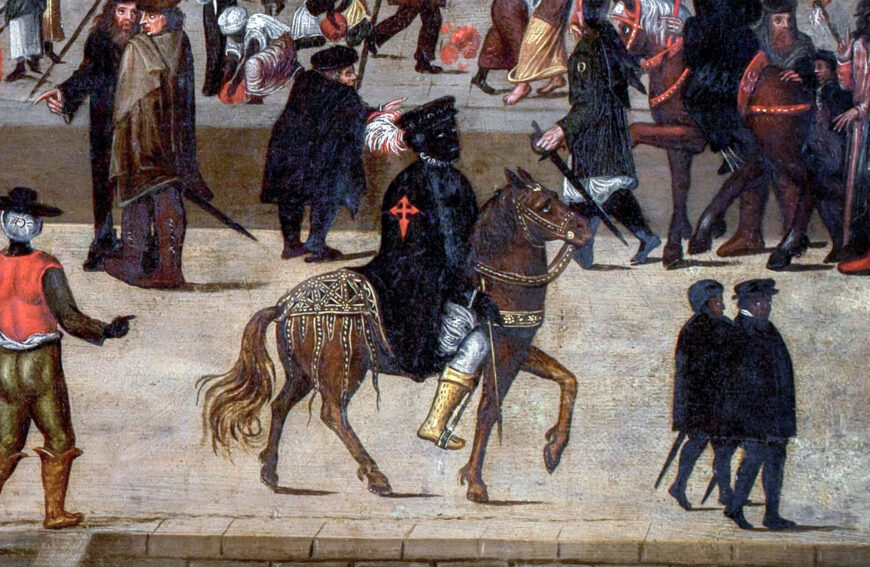
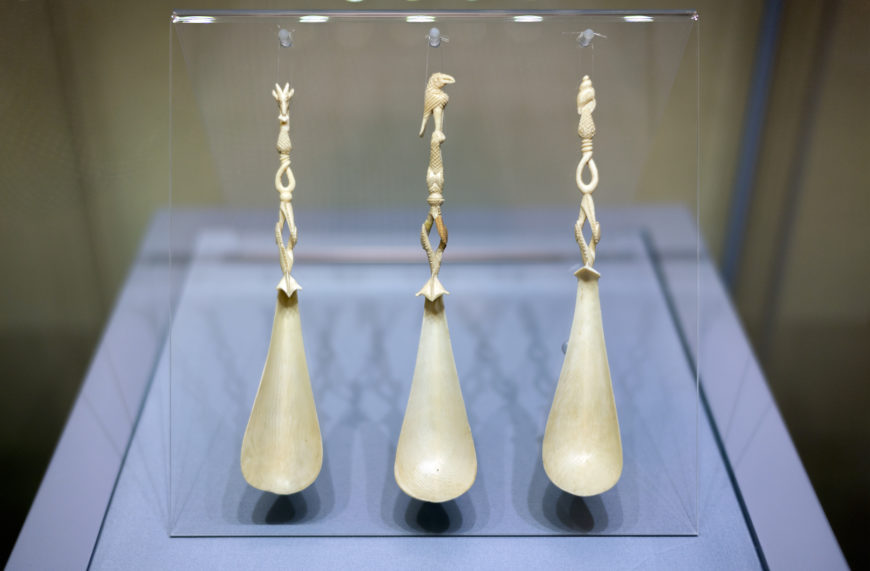
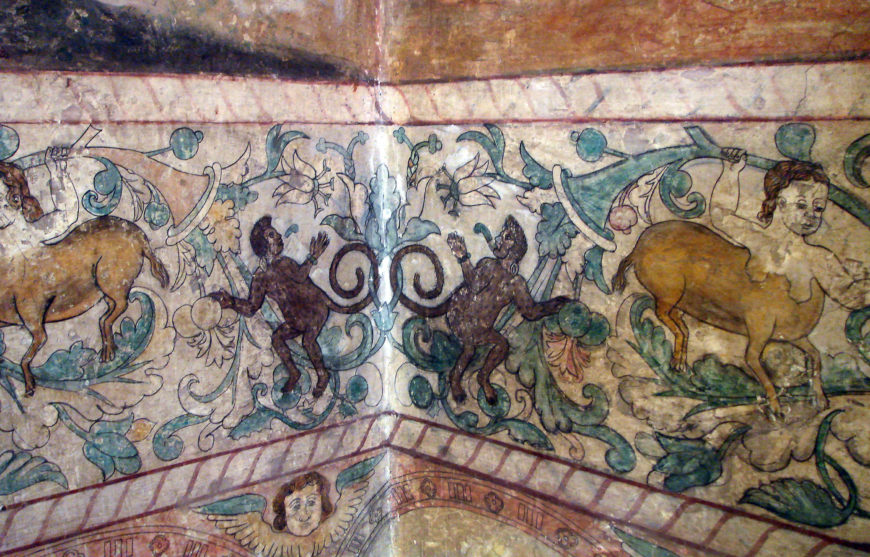
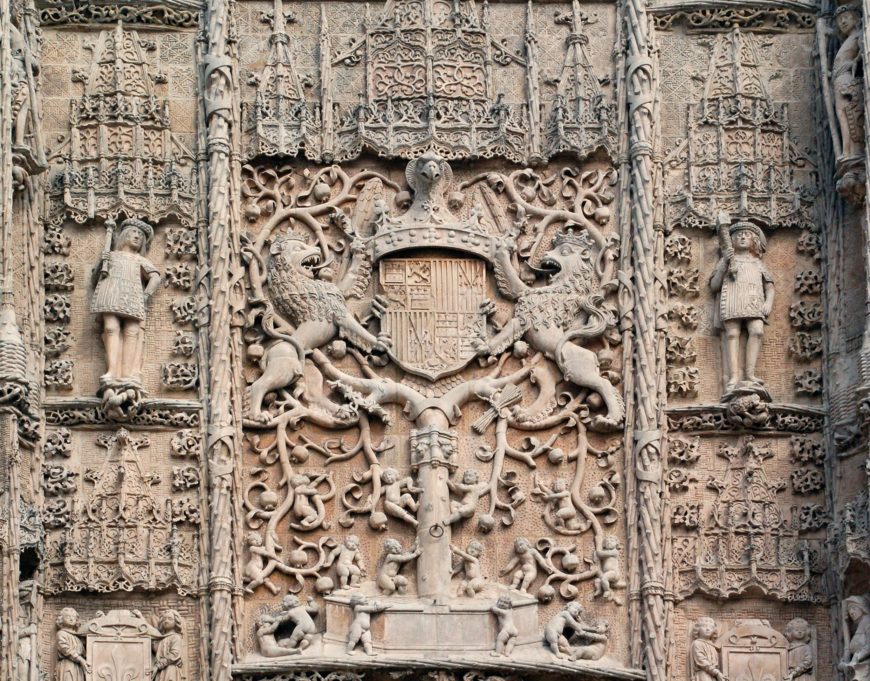
Spanish and Portuguese Renaissance
A style and period first influenced by the Northern Renaissance; later Titian, Raphael, and Bosch became important influences.
Spanish and Portuguese Renaissance
A style and period first influenced by the Northern Renaissance; later Titian, Raphael, and Bosch became important influences.
Basics to get you started
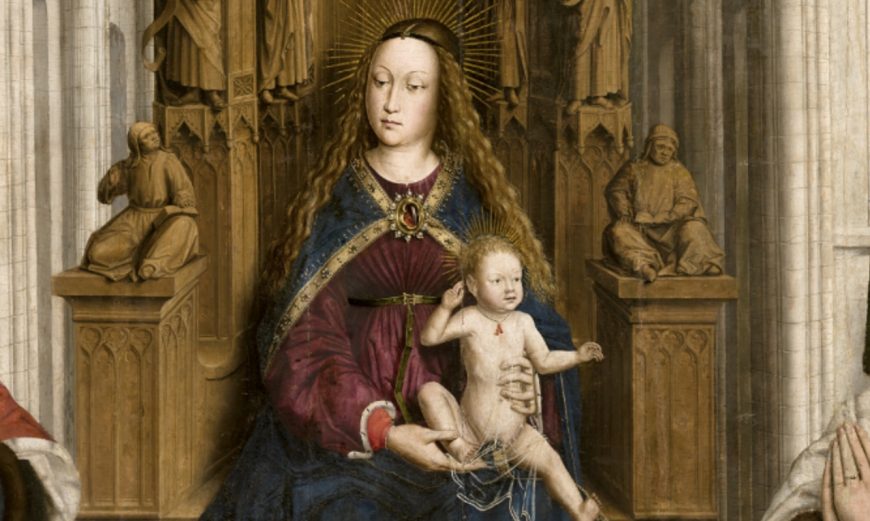

15th-century Spanish painting, an introduction

The rise and fall of the Avis dynasty in Portugal, an introduction

The Renaissance in Spain

The life of Christ in medieval and Renaissance art

Introduction to the Protestant Reformation (part 1 of 4): Setting the stage

Introduction to the Protestant Reformation (part 4 of 4): The Counter-Reformation

Atmospheric perspective explained

Contrapposto explained

Foreshortening explained
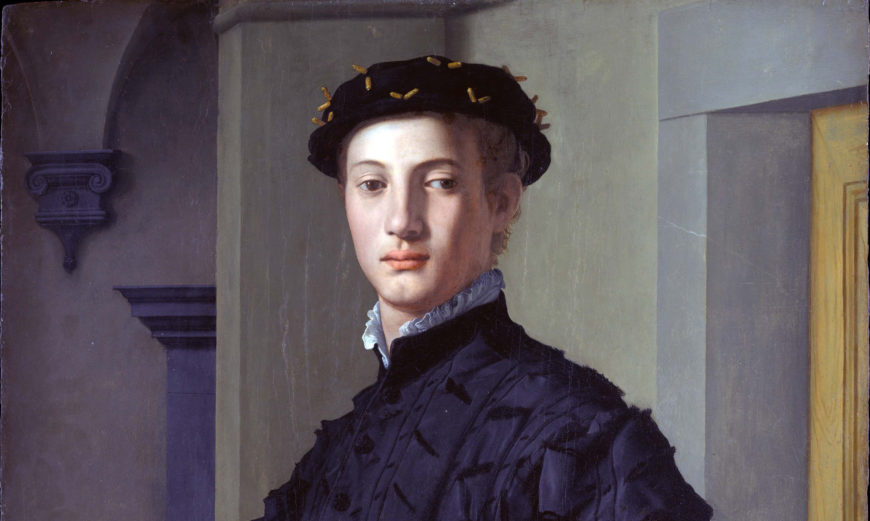

Why commission artwork during the renaissance?
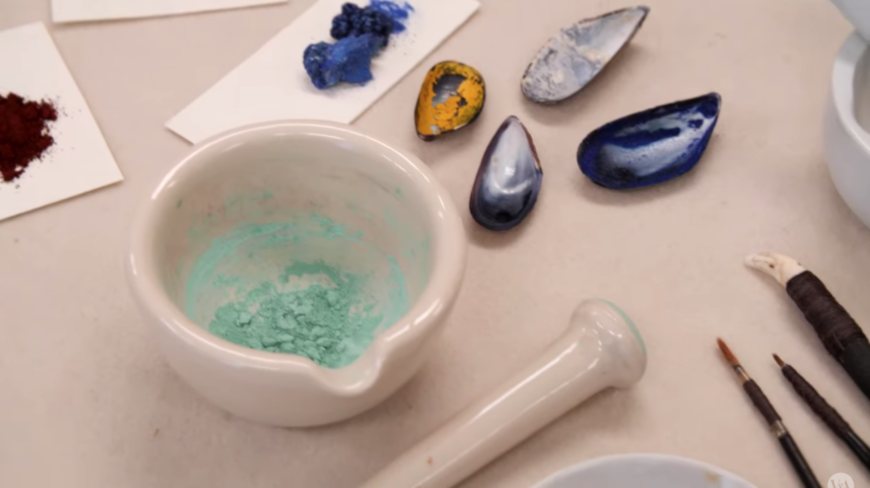

Renaissance watercolors: materials and techniques

Who’s who? How to recognize saints…

Manuscripts: major works of art
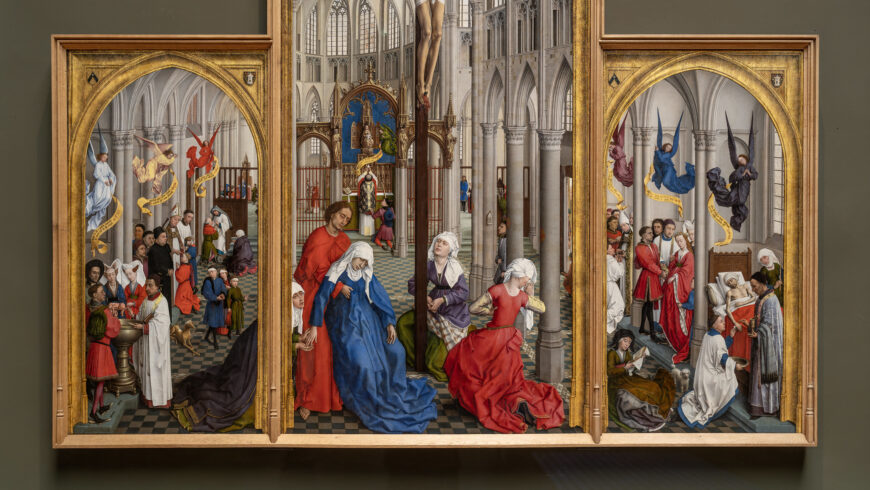

The Medieval and Renaissance Altarpiece

Tiny timeline: global Europe
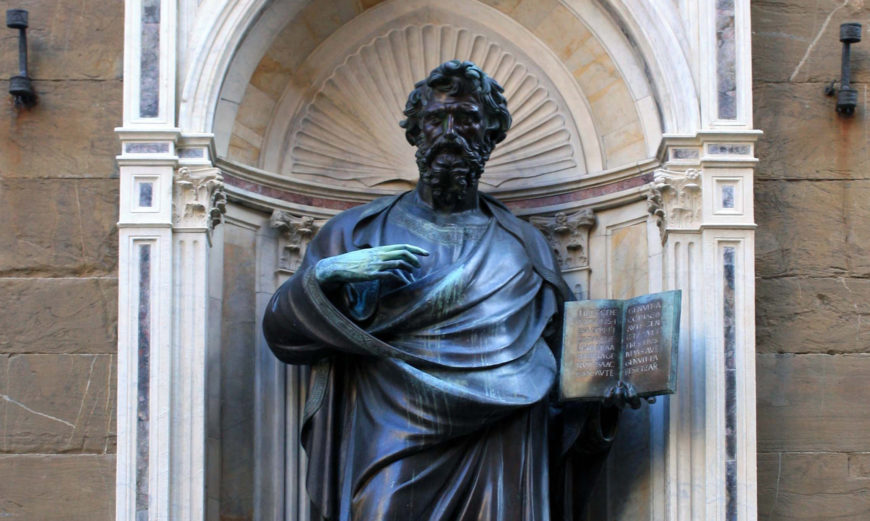

Types of renaissance patronage
Works of Art
Artists

Alejo Fernández, The Virgin of the Navigators, 1531–36, oil on panel (Reales Alcázares, Seville)