The viceroyalty encompassed modern-day Peru as well as much of the rest of South America, the Portuguese controlled what is today Brazil.
1534–1820 C.E.
The viceroyalty encompassed modern-day Peru as well as much of the rest of South America, the Portuguese controlled what is today Brazil.
1534–1820 C.E.
What is the Viceroyalty of Peru?
We're adding new content all the time!
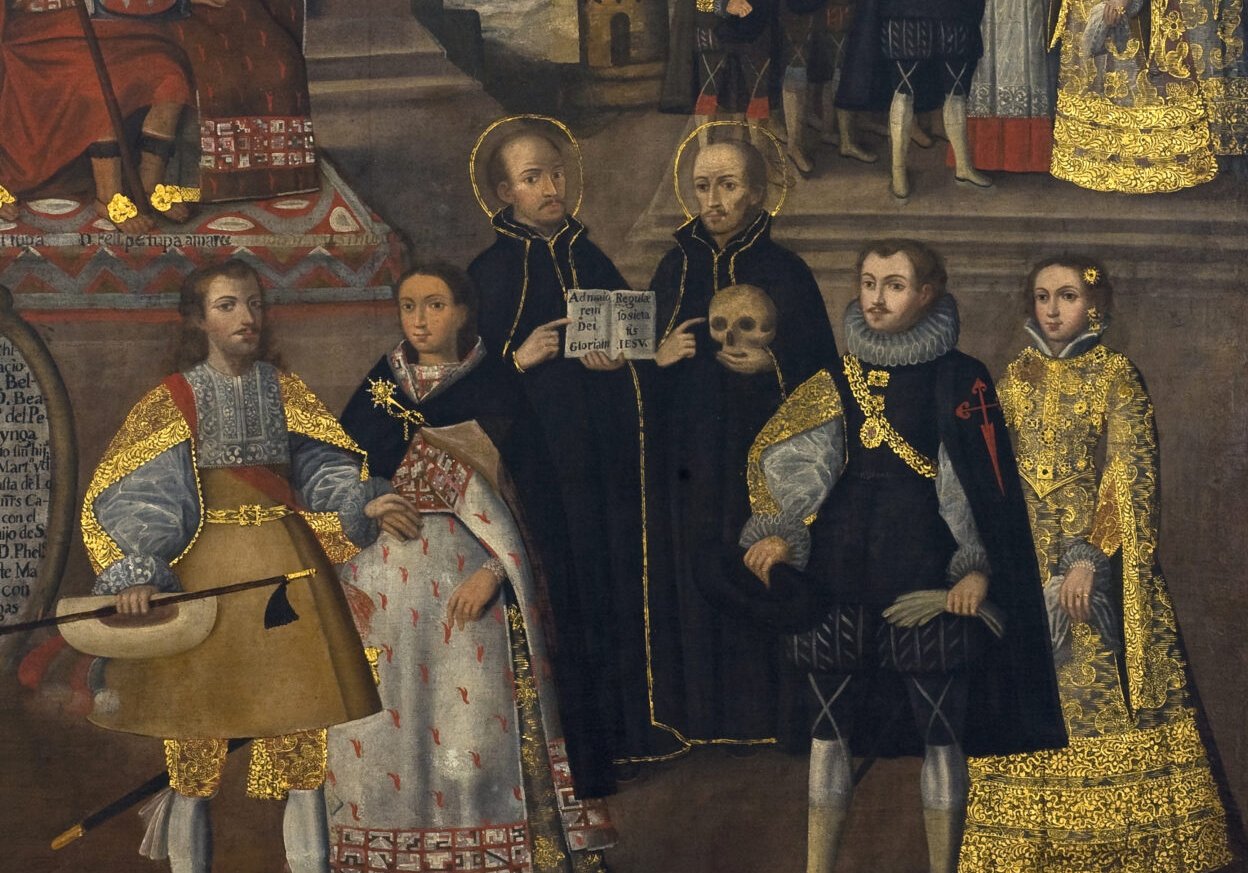

This painting is a fascinating window into the power relations between the Inka, the Jesuits, and the Spanish colonial authorities.
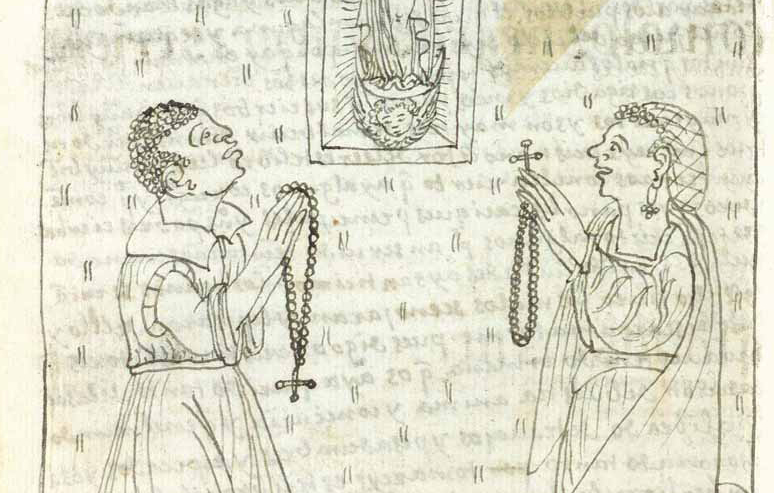
Nueva Corónica provides us with a revealing glimpse at interactions between Africans and Indigenous Andeans in the Viceroyalty of Peru.

Despite violent European invasion and colonization, Indigenous people living in the Andes continued, adapted, resisted, and shaped Peru.
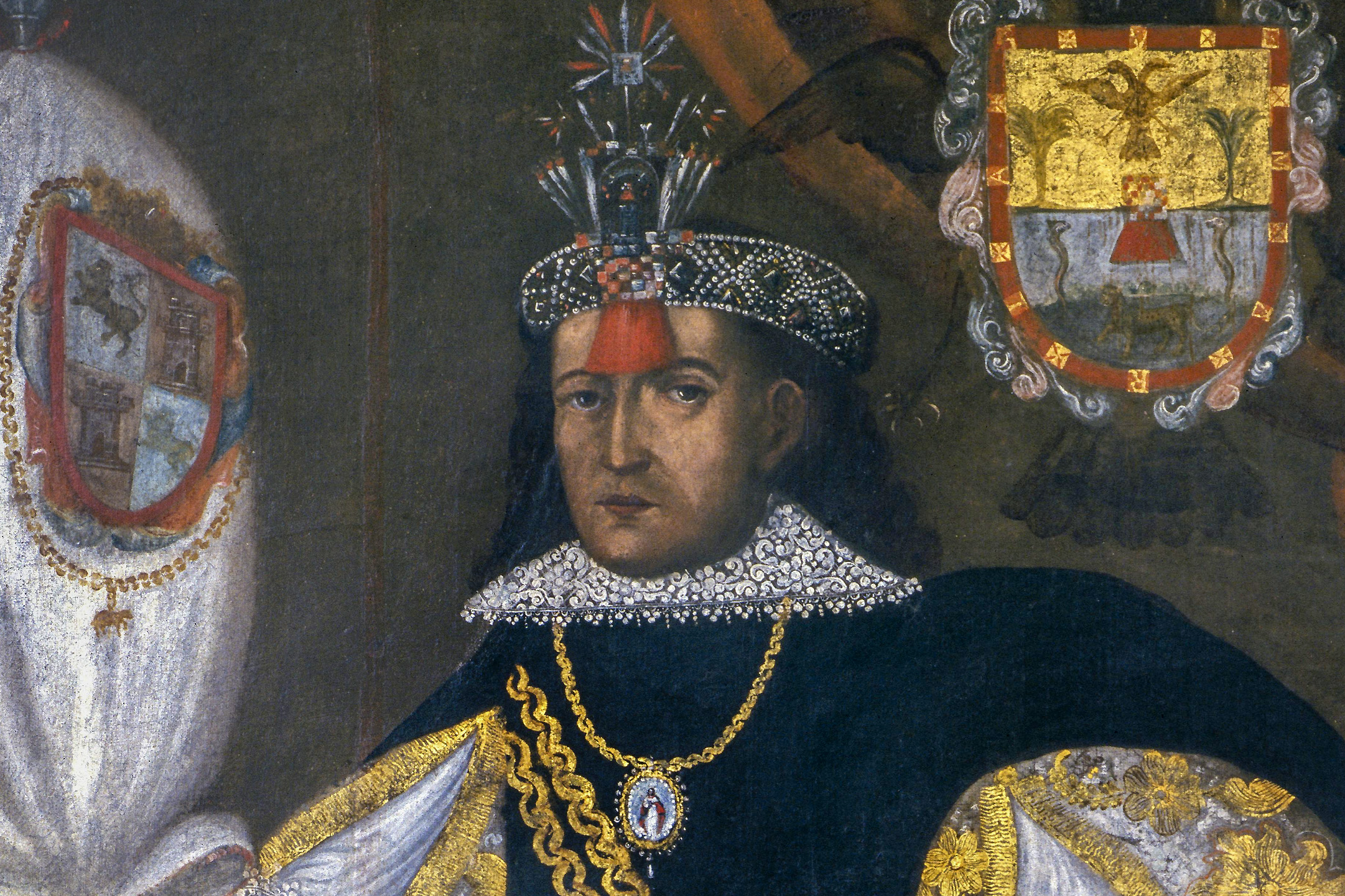

An Indigenous nobleman in colonial Peru, Don Marcos is strategically portrayed with emblems of both Inka and Spanish elite status.

Never underestimate the power of a well-chosen accessory!

These portraits of a couple show us what the sitters want us to see about them, and conceal the less glamorous details of their lives.

This luxuriously dressed Virgin Mary as a child spinning cloth may have spoken to the rich textile traditions of Indigenous cultures in Peru

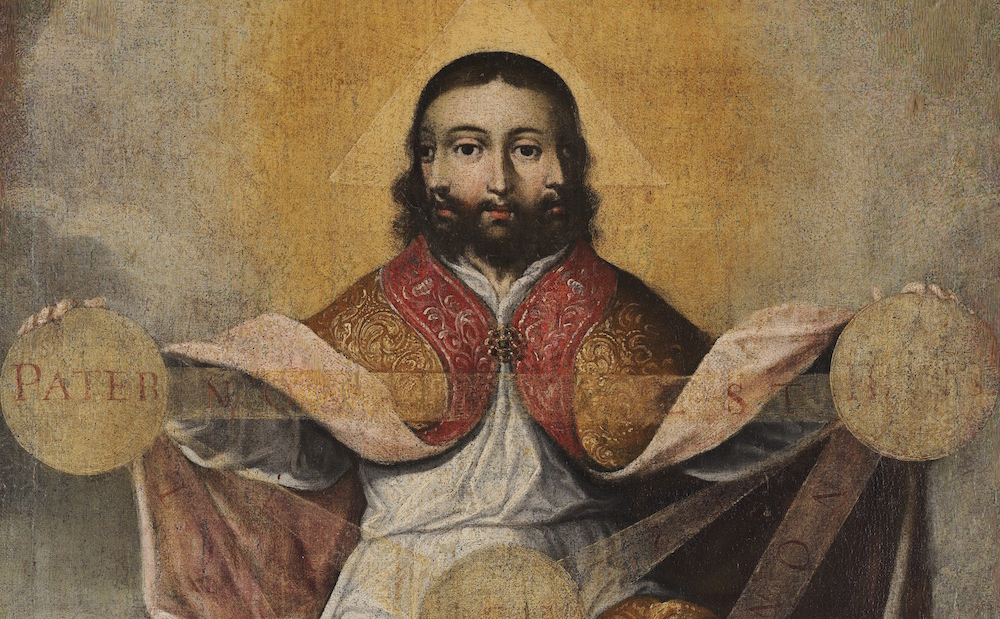
The Trinity visualized as triplets was a common subject in 18th-century Peru—and beyond

The Churches of Chiloé represent a unique example in Latin America of an outstanding form of ecclesiastical wooden architecture.

Pérez de Holguín creates an opulent vision of the city of Potosí, disregarding the infamous stories of poverty and exploitation in the mines of the Cerro Rico

Follow the conservation treatment and research of “Emblem of Folly,” a painting from colonial Cuzco. Committed study of these works can help create a better understanding of Latinx cultural identity and history.
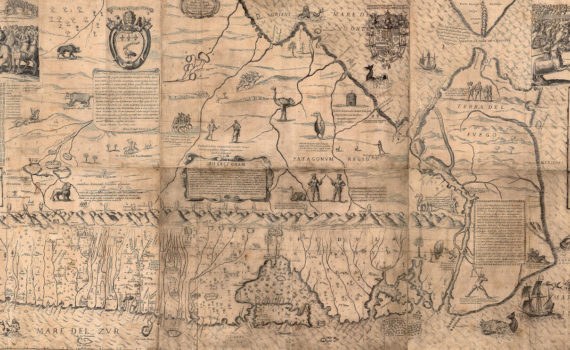
The Ovalle map is one the earliest maps of Chile that circulated around Europe, and includes people, plants, and animals to create a vivid sense of the lands controlled by the Spanish Crown.