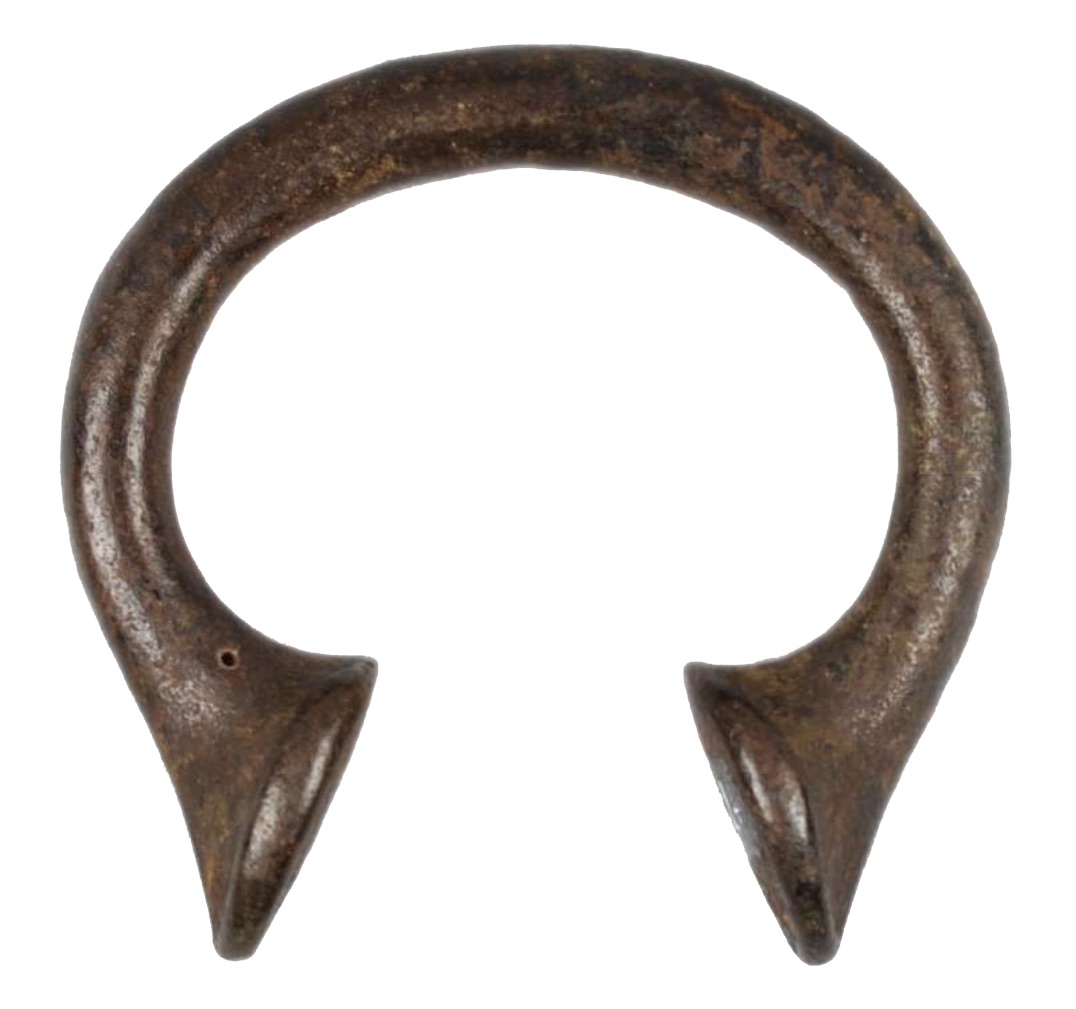
Manilla (bracelet), 19th century C.E., Nigeria, brass (© Trustees of the British Museum)
Brass
Trade with the Portuguese probably encouraged the growth of brass casting in Benin at this time. Although West Africans invented the smelting of copper and zinc ores and the casting of brass at least as long ago as the 10th century, they did not produce enough metal to supply the casting industry of Benin city, which gave such splendor to the king’s palace. The Portuguese found a ready market for brass ingots, often made in the form of bracelets called “manillas.”
These were made in the Low Countries (modern Holland), traded throughout West Africa as a kind of currency, and melted down by the brass workers of Benin. When the Portuguese arrived in Benin, Nigeria, in the 15th century, they quickly started trading brass and copper for pepper, cloth, ivory, and slaves. In the 1490s a Portuguese trader wrote that at Benin copper bracelets were more highly prized than brass ones. [1]
The number of manillas in circulation increased dramatically from the 16th century when they became one of the standard trade currencies. Millions were made in Europe, along with brass and copper pots and pans, and imported into Africa for trade. Research by British Museum scientists has shown that objects like these were melted down and made into works of art such as the Benin bronze plaques.

Brass figure of a Portuguese soldier holding a musket, 17th century C.E., Benin, Nigeria, brass, 43 x 20 x 18.5 cm (© Trustees of the British Museum)
A Portuguese soldier
This is an image of a Portuguese soldier. He wears a typical 16th-century European costume, with steel helmet and sword, and he carries a flintlock gun. Guns were new to the people of West Africa when the Portuguese arrived. So, Africans traded them from Europeans and learned to make them for themselves, to help them in their wars against peoples who still only had hand weapons or bows and arrows. Sometimes the king of Benin even employed Portuguese soldiers, like this man, to fight as mercenaries in his wars. Figures of Europeans such as this Portuguese soldier were kept on royal altars or on the roof of the royal palace in Benin city.
Control of trade
The rulers of Benin fought their neighbors for control to the supply of goods which could be traded to the Europeans on the coast. The king himself was in charge of trading slaves, ivory, and other important goods so that all the profit went to support his court and government. Other merchants could only trade with the king’s permission. To prevent unauthorized trading, Europeans were seldom allowed to travel inland or visit Benin city.
© Trustees of the British Museum
Note:
[1] Thomas Lionel Hodgkin, Nigerian perspectives: An historical anthology (Oxford: Oxford University Press, 1975), p. 121, quoted in Kate Ezra, Royal Art of Benin: The Perls Collection in the Metropolitan Museum of Art, 1992, p. 12. “Duarte Pacheco Pereira, who visited Benin in the 1490s, wrote in his Esmeraldo de Situ Orbis, “The Kingdom of Beny [sic] is about eighty leagues long and forty wide; it is usually at war with its neighbors and takes many captives, whom we buy at twelve or fifteen brass bracelets each, or for copper bracelets which they prize more.”
Additional resources
More from Smarthistory on African art and the effects of European contact and colonization.
Read a Reframing Art History chapter about Portuguese contacts and exchanges.
Paula Girshick Ben-Amos, The art of Benin (London: The British Museum Press, 1995).
Jonathan Williams (ed.), Money: a history (London: The British Museum Press, 1997).
Kenji Yoshida and John Mack (eds.), Images of other cultures (Osaka: National Museum of Ethnology, 1997).