Material splendor
Jan van Eyck’s Rolin Madonna presents a series of objects and surfaces: a fur-lined damask robe, ceramic tiles, a golden crown, stone columns, warm flesh, flowers, translucent glass, and a reflective body of water. Even the air above the distant river seems palpable. The painting is a careful study of how light reacts to the varying textures. But the scene is an imagined one. Before a kneeling man the Virgin presents on her lap the Christ child, and an angel holds a crown above her. No eye contact is made. It is as if we are seeing what the man has in his mind’s eye as he prays from the book in front of him. While the sumptuousness of the surroundings belie the otherworldliness of the Mother and Child, at the same time they seem to augment rather than diminish their divinity. For Nicolas Rolin, the man in this image, it seems that attention to the magnificence and splendor of valuable arts and materials can provide a vision of the sacred, rather than distract from it.
Although Jan van Eyck’s painting is an exceptional artwork, it is typical of fifteenth-century Flemish art in the value it attributes to material splendor. The area of the southern Low Countries was one of the major contributors to what is often referred to as the Northern Renaissance—the efflorescence of artistic production that took place north of the Alps in the fifteenth and sixteenth centuries.
Flemish art
Map of major Flemish-speaking cities during the Northern Renaissance within the outline of modern Belgium
“Flemish art” is a difficult term: medieval Flanders does not have the same borders as it does today. It is used by art historians loosely to refer to artistic production in Flemish speaking towns—particularly Bruges, Ghent, Brussels and Tournai. The term is also most often associated with painting. Painters like Jan van Eyck, Rogier van der Weyden, and Hugo van der Goes were as internationally famous in their time as they are now, finding patrons not only in the Low Countries (today Netherlands, Belgium and northern Germany), but in Italy also, where their oil-paint technique had a considerable influence.
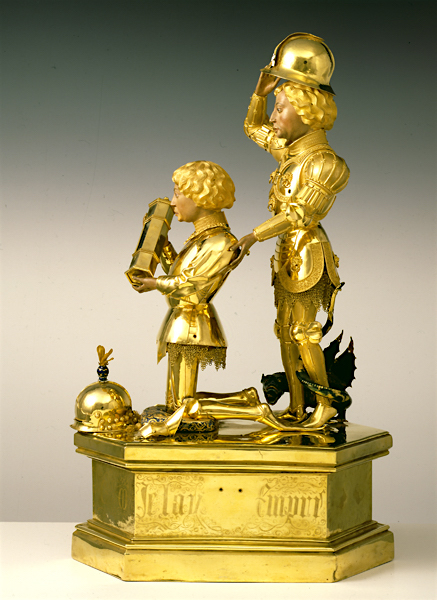

Gérard Loyet, Reliquary of Charles the Bold (with St. George), 1467-71, gold, vermeil and enamel, 53 x 17.5 x 32 cm (Cathedral of Liège)
However, just as van Eyck was attentive to the range of crafted objects in the Rolin Madonna, we too should be observant of the many arts practiced in fifteenth-century Flanders. There were workshops across the major towns of Flanders for goldsmiths, ceramicists, cabinet-makers, manuscript illuminators, tapestry weavers, and sculptors in wood and stone.
More than paintings
The most expensive artworks were tapestries and goldwork and nobles would commission these as gifts for their allies and relatives. The prominence painting is given today is partly because our culture values painting as a “fine art” alongside sculpture and architecture, and thus one distinct from the “decorative” or “applied” arts of other media. It is important to understand that these distinctions did not exist in the fifteenth-century Low Countries. Therefore, when visiting collections in search of Netherlandish art, also take time to seek out the rare surviving goldwork, tapestries, and sculpture. Singular pieces include the Liège statuette (a reliquary with images of Charles the Bold and St George in the Cathedral of Liège), the Burgundian tapestries at Bern Historical Museum, and the tombs of Mary of Burgundy and Charles the Bold in the Church of our Lady in Bruges.
A major trading center
To understand why Flanders became the site of such intensive artistic production in the fifteenth century, it is useful to consider its place within the wider western European economy. Flanders was the most urbanized region of northern Europe in the fourteenth and fifteenth centuries. Between c. 1000 and 1300, its town and ports grew in size and number as it became the major center for trade in northern Europe, acting as a nodal point for merchants from England, the Baltic, Italy, and France. For this reason, its cities, particularly Bruges and Ghent, became centers of artistic production.
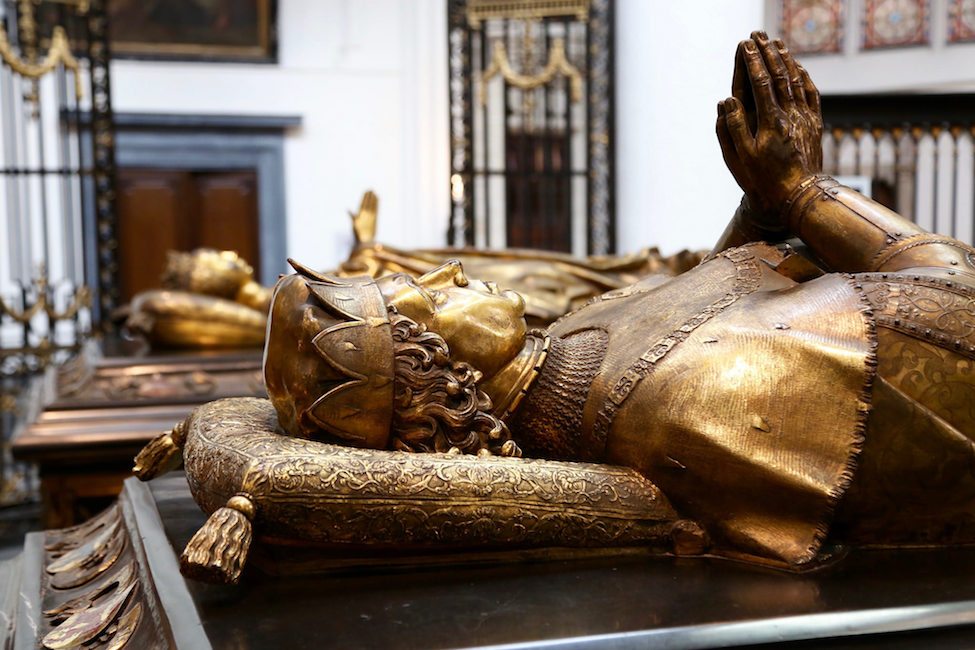

Tombs of Mary of Burgundy and Charles the Bold in the Church of our Lady in Bruges (photo: Alexey Yakovlev, CC BY-SA 2.0)
Craftsmen of all types—including painters, tapestry manufacturers, manuscript illuminators, goldsmiths, and sculpture in wood and stone—could rely on the trade networks that brought raw materials to these cities. Painters and sculptors established their own workshops and joined guilds that regulated the quality of their products, the prices for which they could be sold, as well as license those allowed to practice these crafts. The towns themselves often acted as a patrons, often commissioning sculpture and coats-of-arms for their municipal buildings. Particularly wealthy citizens also acted as patrons for some of the most famous Flemish paintings: Hubert and Jan van Eyck’s famous Ghent Altarpiece, made in 1432 for Ghent’s cathedral of Saint Bavo, was financed by the Ghent merchant Jodocus Vijd; the Italian banker and Bruges resident Tommaso Portinari was the patron of van der Goes’s Portinari Altarpiece; whereas the guild of archers of Leuven commissioned van der Weyden’s Descent from the Cross.
The Flemish towns therefore functioned as a crucible for both the highly specialized workshop labor needed to produce high-quality paintings, goldwork, textiles, and sculptures, and for the wealthy patrons that the craftsmen relied on. The fifteenth-century efflorescence of art in Flanders also coincided with the demographic recovery after the shock of the Black plague in the mid-fourteenth century. In addition, the wars between France and England, which had slowed the Flemish economy, gradually subsided during this period. But these were not the only factors in the development of Flemish visual art. Another major source of patronage came from the Burgundian court.
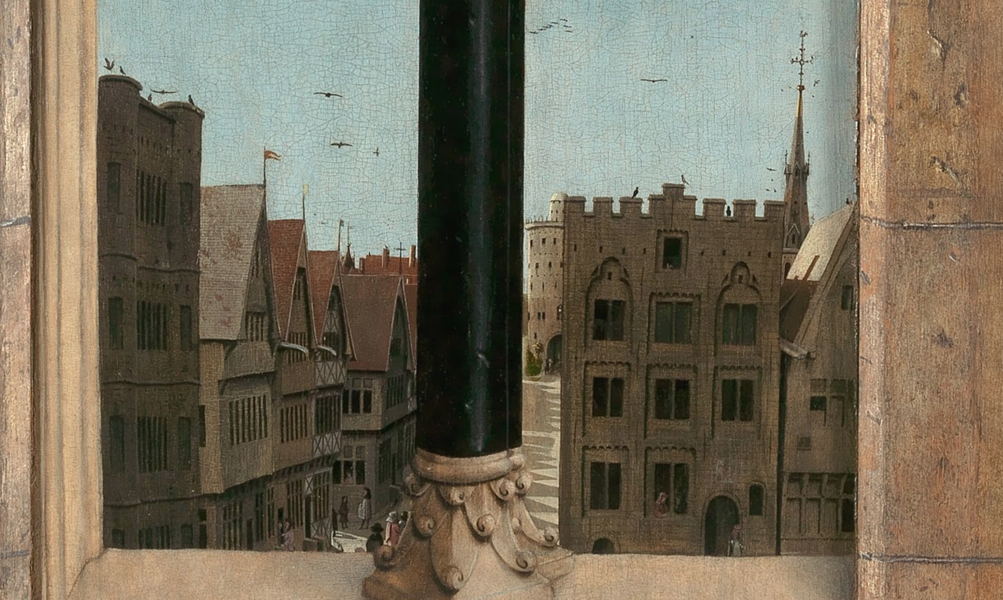

Detail showing a street in Ghent, Jan van Eyck, from the Annunciation scene in the Ghent Altarpiece (closed) after restoration, 1432 (Saint Bavo’s cathedral, Ghent)
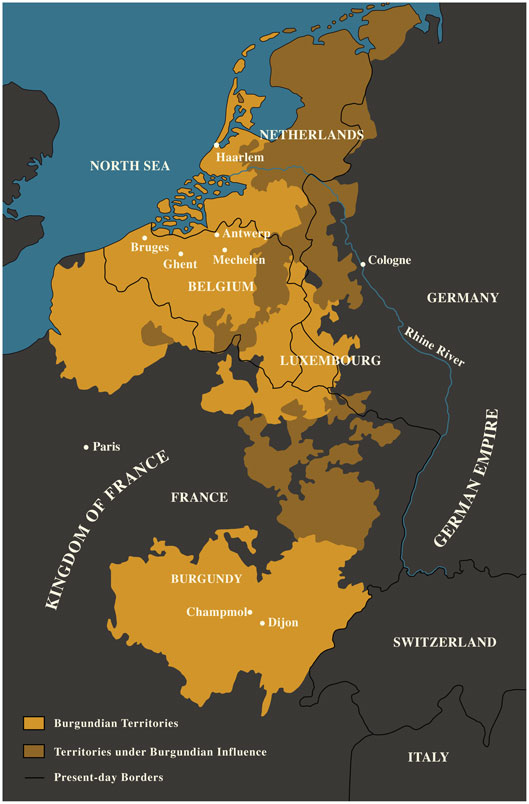
Map of Burgundy (source)
Part of the Burgundian court
In 1384 the count of Flanders, Louis II, died, and he was succeeded by his son-in-law, Philip the Bold, the fourth son of King John II of France and the Duke of Burgundy. Flanders was from then ruled by a series of Burgundian dukes, and many craftsmen from the Flemish towns were enlisted by the Burgundian court where they would work for the duke and his courtiers. To return to where we began, Nicolas Rolin, the man depicted in Van Eyck’s Rolin Madonna and the patron of that painting, was a high-ranking Burgundian courtier. In addition to being a patron of van Eyck, he also commissioned van der Weyden to make a large altarpiece for the hospice he endowed in Beaune (where it can still be seen).
After the death of Duke Charles the Bold in 1477, the Burgundian lands were partitioned between France and the Holy Roman Empire, and many Netherlandish artists lost the court’s patronage as a result. Furthermore, the towns of Bruges and Brussels were losing their economic importance to Antwerp, and the painters there favored a quicker method of painting suited for widespread sale on that city’s international markets, rather than the slower, more layered and labored technique of their forebears. However, the influence of fifteenth-century Netherlandish painting would continue into the next century, particularly in the closely observed still life and portrait paintings by court artists such as Hans Holbein the Younger and Albrecht Dürer.
Additional resources:
Northern European Painting of the 15th-16th centuries from the National Gallery of Art
Burgundian Netherlands on The Metropolitan Museum of Art’s Heilbrunn Timeline of Art History
Jan van Eyck on The Metropolitan Museum of Art’s Heilbrunn Timeline of Art History
Early Netherlandish Painting on The Metropolitan Museum of Art’s Heilbrunn Timeline of Art History
Guy Delmarcel, Flemish Tapestry from the 15th to the 18th Century, trans. Alastair Weir (Tielt, 1999)
Craig Harbison, The Mirror of the Artist: Northern Renaissance Art in its Historical Context (New York, 1995)
Craig Harbison, Jan van Eyck: The Play of Realism (2nd ed.; London, 2012)
Susie Nash, Northern Renaissance Art (Oxford, 2008)
James Snyder, Northern Renaissance Art: Painting, Sculpture, the Graphic Arts from 1350 to 1575 (2nd ed.;New York, 2005)
Hugo Van der Velden, The Donor’s Image: Gerard Loyet and the votive portraits of Charles the Bold (Turnhout, 2000)


