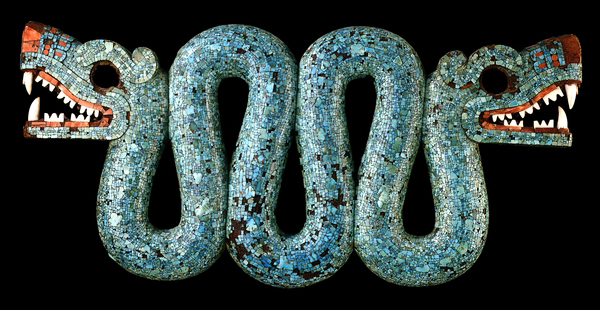
Mosaic of a Double-headed Serpent, c. 15th-16th century, cedrela wood, turquoise, pine resin, oyster shell, hematite, and copal, 20.5 x 43.3 x 6.5 cm, Mexico © Trustees of the British Museum
An icon of Mexica (Aztec) art, this striking object was probably worn on ceremonial occasions as a pectoral (an ornament worn on the chest). It is carved in wood (Cedrela odorata) and covered with turquoise mosaic. The wood is hollowed at the back.
Serpent imagery
Serpent imagery occurs throughout the religious iconography of Mesoamerica. The serpent played a very important role in Aztec religion. The word for serpent in Nahuatl, the language spoken by the Aztecs, is coatl and is associated with several gods such as Quetzalcoatl (Feathered Serpent), Xiuhcoatl (Fire Serpent), Mixcoatl (Cloud Serpent) or Coatlicue (She of the Serpent Skirt), the mother of the Aztec god Huitzilopochtli. The habit of snakes to shed their skin each year probably led to them being used to convey ideas concerning renewal and transformation. Likewise the ability of many species to move freely between water, earth and the forest canopy helped underline their symbolic role as intermediaries between the different layers of the cosmos (underworld, earth and sky).
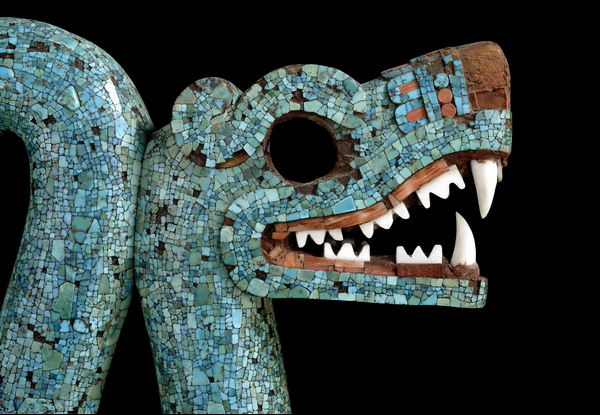

Head of Serpent (detail), Mosaic of a Double-headed Serpent, c. 15th-16th century, cedrela wood, turquoise, pine resin, oyster shell, hematite, and copal, 20.5 x 43.3 x 6.5 cm, Mexico © Trustees of the British Museum
The word coatl is also part of many place names, such as Coatepec (“the hill of the serpents”). Coatepec is the birthplace of the god Huitzilopochtli, the principal Aztec god, and thus one of the most important places in Aztec mythology.

Back of Serpent (detail), Mosaic of a Double-headed Serpent, c. 15th-16th century, cedrela wood, turquoise, pine resin, oyster shell, hematite, and copal, 20.5 x 43.3 x 6.5 cm, Mexico © Trustees of the British Museum
Serpents were also used as architectural elements, for example, a wall of serpents (coatepantli) was often used to mark out sacred spaces within a ceremonial area. At the Aztec capital, Tenochtitlan, such a wall surrounded part of the Great Temple, which was the ritual focus for the entire city.
Materials
Spondylus (thorny oyster) shell was used for the bright red details around the nose and mouth of both of this object’s serpent heads. Strombus (conch) shell was used for the white teeth. Within the gaping mouths the resin adhesive was colored bright red with hematite. Beeswax adheres to the edges of the empty eye sockets which were probably originally inlaid, perhaps with iron pyrites.
The reverse of the body is undecorated, although the surface may have originally been gilded, but the heads are worked in mosaic on both sides. Resins from pine and Bursera (copal) were used as adhesives for the mosaic.
Suggested readings:
C. R. Cartwright and N. D. Meeks, “Aztec conch shell working: high- tech design,” British Museum Technical Research Bulletin 1, (2007), 35-42.
C. McEwan, A. Middleton, C.R. Cartwright, R. Stacey, Turquoise mosaics from Mexico (London, The British Museum Press, 2006).
C. McEwan, Ancient Mexico in the British Museum (London, The British Museum Press, 1994).
R. J. Stacey, C. R. Cartwright and C. McEwan “Chemical Characterization of Ancient Mesoamerican ‘Copal’ Resins: Preliminary Results.” Archaeometry 48, (2006), 323-340.
© Trustees of the British Museum

